A Zebrafish Chemical Suppressor Screening Identifies Small Molecule Inhibitors of the Wnt/beta-catenin Pathway
- Authors
- Nishiya, N., Oku, Y., Kumagai, Y., Sato, Y., Yamaguchi, E., Sasaki, A., Shoji, M., Ohnishi, Y., Okamoto, H., Uehara, Y.
- ID
- ZDB-PUB-140513-245
- Date
- 2014
- Source
- Chemistry & Biology 21: 530-40 (Journal)
- Registered Authors
- Nishiya, Naoyuki, Okamoto, Hitoshi, Sato, Yuki
- Keywords
- none
- MeSH Terms
-
- Small Molecule Libraries/chemistry
- Small Molecule Libraries/pharmacology*
- Structure-Activity Relationship
- Animals
- Alkyl and Aryl Transferases/antagonists & inhibitors*
- PubMed
- 24684907 Full text @ Chem. Biol.
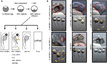
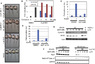
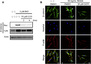
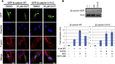
Genetic screening for suppressor mutants has been successfully used to identify important signaling regulators. Using an analogy to genetic suppressor screening, we developed a chemical suppressor screening method to identify inhibitors of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. We used zebrafish embryos in which chemically induced β-catenin accumulation led to an "eyeless" phenotype and conducted a pilot screening for compounds that restored eye development. This approach allowed us to identify geranylgeranyltransferase inhibitor 286 (GGTI-286), a geranylgeranyltransferase (GGTase) inhibitor. Our follow-up studies showed that GGTI-286 reduces nuclear localization of β-catenin and transcription dependent on β-catenin/T cell factor in mammalian cells. In addition to pharmacological inhibition, GGTase gene knockdown also attenuates the nuclear function of β-catenin. Overall, we validate our chemical suppressor screening as a method for identifying Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitors and implicate GGTase as a potential therapeutic target for Wnt-activated cancers.