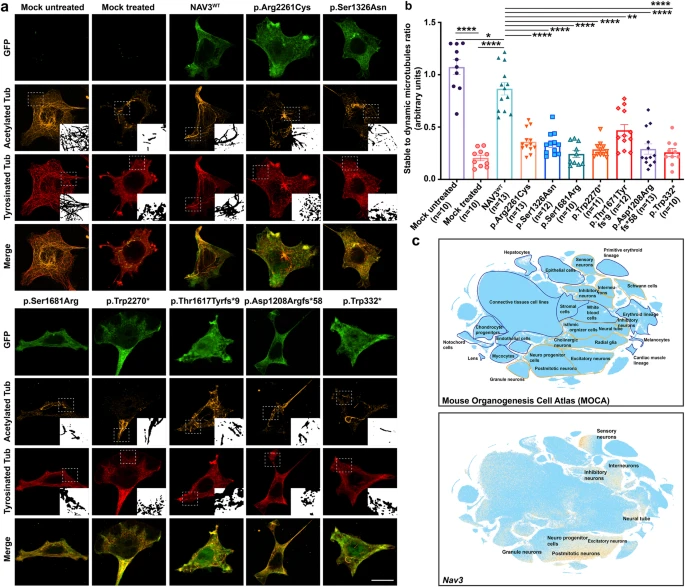
Fig. 4 ID-associated variants impact NAV3 ability to stabilize microtubule in HEK293T cells. a Representative confocal images of GFP-NAV3 wild type (WT) and mutated proteins (green) overexpressing HEK293T cells treated with 10 μM nocodazole for 1 h, and immuno-labeled with microtubule acetylated tubulin (orange) and tyrosinated tubulin (red) markers. Compared to cells over-expressing WT GFP-NAV3 with a stable microtubular network despite the nocodazole treatment, all the ID-associated variants impact the microtubule-stabilization function of NAV3. Dotted white lines show zoomed in areas in insets. Scale bar: 20 μm. b Bar graph quantification ratio of stable to dynamic microtubules for all respected treated groups. At least 10 transfected cells per construct were imaged and quantified. All the variants expressing cells results were compared to WT using the paired student t-test. NAV3 proteins harboring ID-associated variants showed significantly reduced microtubules stability (**** p < 0.0001; *p < 0.0350; **p < 0.00220). Error bars represent standard error of the mean. c Single-cell RNA (sc-RNA) expression profile of mouse cell clusters at early organogenesis (top panel) generated from transcriptomes of around 2 million cells derived from 61 embryos staged between 9.5 and 13.5 days of gestation (data available from UCSC cell browser). The transcriptome data (bottom panel) shows the highest expression of Nav3 in the neural tube and postmitotic neurons, while expression also observed in inhibitory and inter neurons. Dispersed expression in neuronal progenitor cells were also observed.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Commun Biol