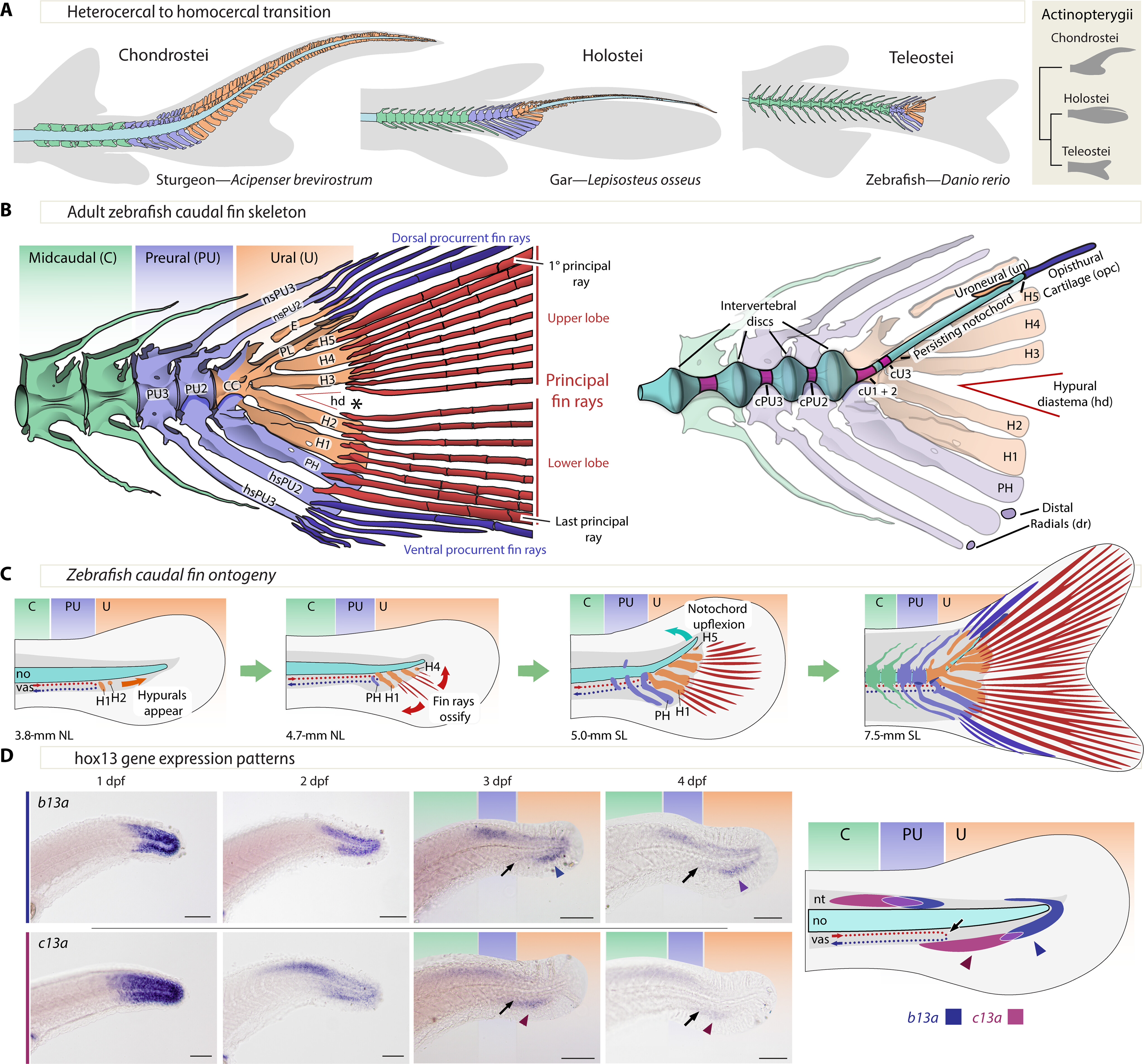
Fig. 1 Zebrafish caudal anatomy, development, evolution, and b13a and c13a expression. (A) Representative caudal fin morphologies in actinopterygians, featuring gray-shaded body contour and fin rays, with midcaudal, preural, and ural elements in green, blue, and orange, respectively. (B) Left: Adult zebrafish caudal fin skeleton, highlighting the three regions of the caudal fin and the separation of upper and lower principal rays (asterisk, *). Right: Description of internal elements within the caudal fin skeleton, including the notochord. (C) Developmental relocation of the zebrafish caudal fin elements following bending of the notochord and the appearance of principal fin rays. (D) In situ hybridizations showing b13a and c13a transcripts from 1 to 4 days postfertilization (dpf) and schematic representation of expression domains of both genes at 4 dpf. Black arrows indicate the end of the caudal artery at the PU-U boundary, while blue and red arrowheads mark the ventral expression domains of b13a and c13a, respectively. Scale bars, 0.1 mm. CC, compound centrum; cPU2 and cPU3, preural chordacentra 2 and 3; cU1 to cU3, ural chordacentra 1 to 3; dr, distal radial; E, epural; H1 to H5, hypurals 1 to 5; hd, hypural diastema; hsPU2 and hsPU3, haemal spines of the preural centra 2 and 3; nsPU2 and sPU3, neural spines of the preural centra 2 and 3; NL, notochordal length; no, notochord; opc, opisthural cartilage; PH, parhypural; PL, pleurostyle; PU2 and PU3, preural centra 2 and 3; SL, standard length; un, uroneural; vas, vasculature.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Sci Adv