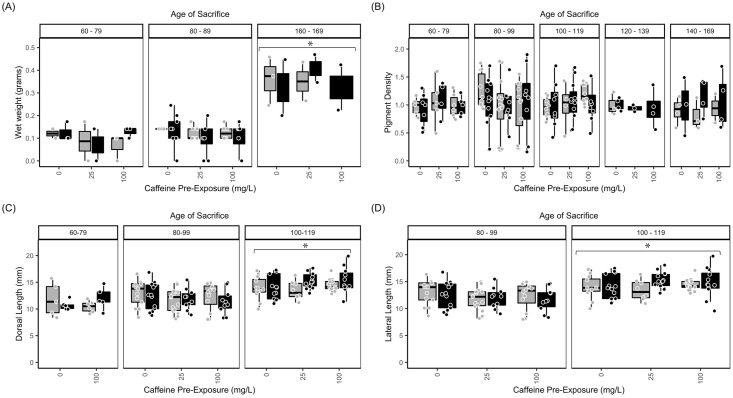
Fig 1 Acute 7-day exposure to caffeine and/or ethanol does not alter length or weight.
(A) Wet weight (g), (B) pigment density, (C) dorsal length (mm), and (D) lateral length (mm) measurements of zebrafish co-exposed to caffeine and ethanol. Measurements were taken immediately after the 7-d exposure period. Measurements were pooled to assess the effect of age of sacrifice across these experimental conditions. Exposure ages (dpf) are indicated at the top of the bar graphs. Black bars = 1.5% ethanol; gray bars = control (0% ethanol). Caffeine exposures (0, 25, or 100 mg/L) are given along the x-axis. Data from individual fish were assessed in age bins to facilitate comparisons: 60–79 dpf (juveniles); 80–99 dpf (young adult); 100–119; 120–139; 140–169 dpf (adult). Wet weight was collected from 60–79 dpf, 80–89 dpf, and 160–169 dpf fish only, to identify the largest differences. Neither caffeine nor ethanol exposure affected measurements. However, age-dependent differences were noted (asterisks). The boxplots show the minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum values for each measure after outliers were removed. For weight (A), there were 3 independent replicates per treatment condition (each ethanol/caffeine dose) for a total of 18 subjects. For all other parameters (B, C, D) there were 7–9 independent replicates per treatment condition for a total of 51 subjects. ANOVA tables and multiple comparison results for this data can be found in