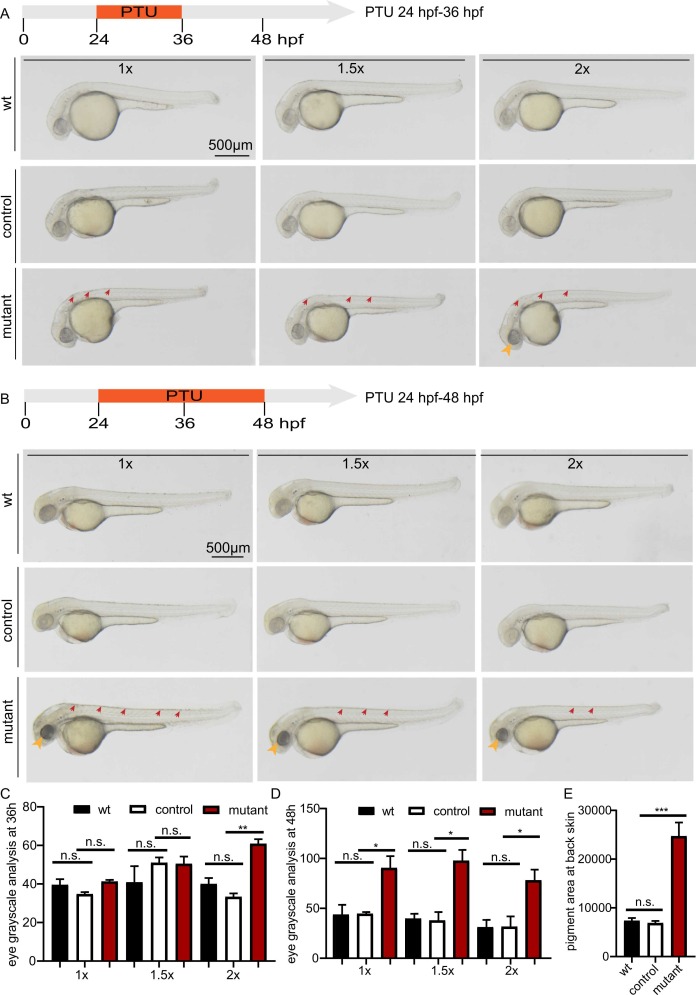
Fig. 1 The pigment phenotype compared among wild-type embryos (wt), slc30a1 sibling controls (control) and slc30a1 double mutants (mutant). A-B, The embryonic phenotypes under a stereomicroscope with PTU treatment at different concentrations (1 ×, 4925 nmol; 1.5 ×, 7388 nmol; 2 ×, 9850 nmol) from 24 to 36 hpf (A) or 24–48 hpf (B). Note the remaining pigments in the eyes (yellow arrows) and back skin (red arrows) in mutant embryos.C-D, Quantitative analysis based on grayscale measurement of the pigments in eyes with PTU treatments from 24 to 36 hpf (C) or from 24 to 48 hpf (D). E, Quantitative analysis based on the pigment size in the embryonic back skin with 1 × PTU treatment from 24–48 hpf. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and n.s., not significant. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Eur. J. Cell Biol.