Fig. 3
Figure 3. RAG2 abolishes aggregation through direct interaction with RAG1
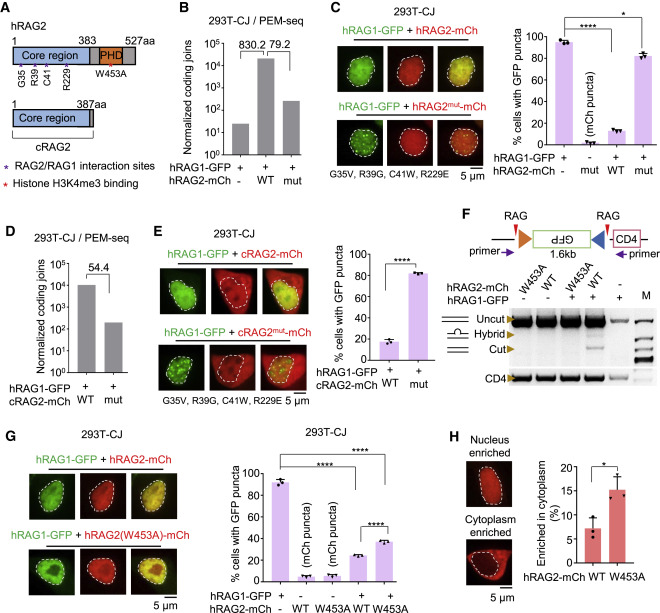
(A) Schematic diagram of RAG2 and cRAG2.
(B) Normalized coding joins detected by PEM-seq in 293T-CJ cells with indicated proteins. Fold changes are indicated. Replicate n = 1.
(C) Representative microscopy images of RAG1-GFP coexpressed with mutated RAG2-mCh in 293T-CJ cells. Mutation sites at the interface of RAG2 are indicated. Bar graph shows the percentage of cells with puncta; replicates n = 3; t test; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Scale bar: 5 μm.
(D) Normalized coding joins detected by the PEM-seq of hRAG1 with cRAG2 or cRAG2mut in 293T-CJ cells. Fold changes are indicated. Replicate n = 1.
(E) Representative microscopy images of RAG1-GFP coexpressed with mutated cRAG2-mCh in 293T-CJ cells. Percentages are on the right. Replicates n = 3; t test; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Scale bar: 5 μm.
(F) Quantitation of the catalytic activity of RAG1-GFP coexpressed with indicated forms of RAG2-mCh in 293T-CJ cells by PCR.
(G) Representative microscopy images of indicated proteins in 293T-CJ cells. Percentages are on the right. Replicates n = 3; t test; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Scale bar: 5 μm.
(H) Distribution of wild-type or W453A of RAG2-mCh in 293T-CJ cells. Percentages are on the right. Replicates n = 3; t test; ∗p < 0.05. Scale bar: 5 μm.
All error bars represent mean ± SD. See also Figure S5.