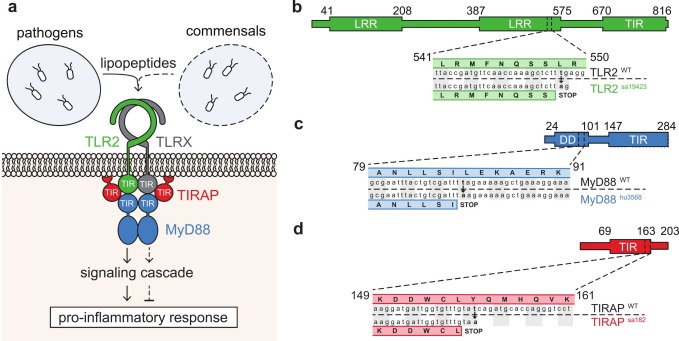
Fig. 1 Fig. 1. Mutant zebrafish lines in the TLR2 signaling pathway. (a) Schematic representation of TLR2 with its adaptor proteins MyD88 and TIRAP (Mal). The Toll/IL-1 receptor (TIR) domain of MyD88 and TIRAP (Mal) can interact with the TIR domain of TLR2. Pathogens have been found to induce pro-inflammatory immune responses via TLR2 (solid line), while commensal microbiota have been shown to dampen pro-inflammatory responses via TLR2 (dashed line). (b-d) Mutant and wildtype alleles with encoded proteins for TLR2 (tlr2sa19423 mutant allele) (b); MyD88 (myd88hu3568 mutant allele) (c); and TIRAP (Mal) (tirapsa182 mutant allele) (d). In all mutant alleles, a threonine to alanine point mutation results in a premature stop codon prior to or inside of the open reading frame for the TIR domain. As a consequence, the mutants produce truncated versions of TLR2, MyD88 or TIRAP, lacking a functional TIR domain. Abbreviations: DD, death domain; LRR, leucine rich repeat; Mal, MyD88 Adaptor-Like; MyD88, Myeloid Differentiation factor 88; TIR, Toll/IL-1 receptor domain; TIRAP, Toll/Interleukin-1 Receptor domain-containing Adaptor Protein; TLR, Toll-Like Receptor.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf.