Fig. 1
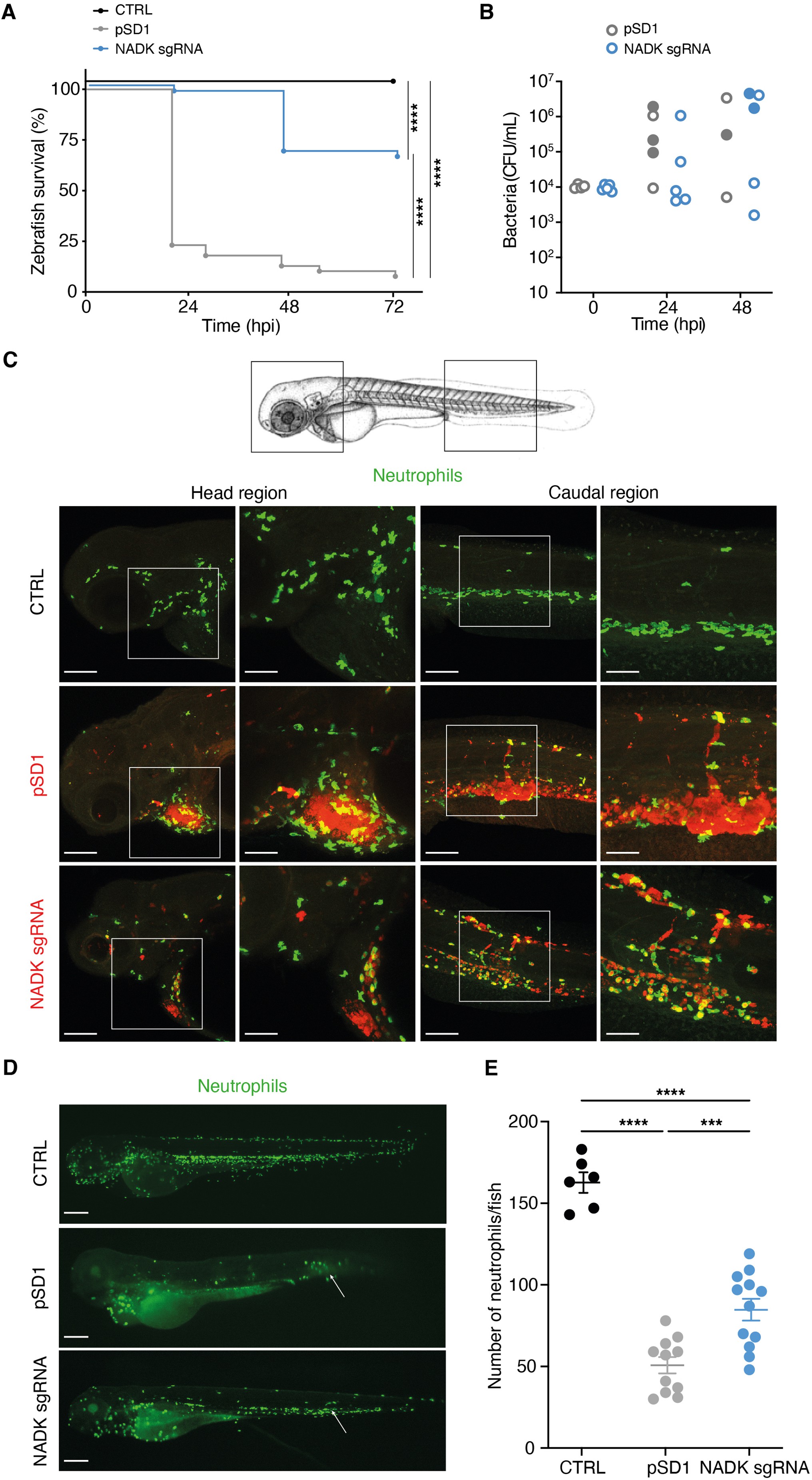
(A) Survival of zebrafish larvae uninfected (CTRL) or intravenously injected at 60 hpf with 104 S. aureus containing the empty vector (pSD1) or the NADK knockdown strain (NADK sgRNA) between 0 and 72 hpi (n=48). (B) Bacterial burden in zebrafish larvae upon intravenous injection with 104 S. aureus containing the empty vector (pSD1) or the NADK knockdown strain (NADK sgRNA). For each strain, CFU was determined in living larvae (open circles) or dead larvae (filled circles) 0, 24, and 48 hpi. (C) Representative fluorescence confocal images of transgenic mpx:GFP zebrafish larvae uninfected (CTRL), or intravenously injected with 104 S. aureus containing the empty vector (pSD1) or the NADK knockdown strain (NADK sgRNA) at 12 hpi. Maximum intensity Z-projection images (2 μm serial optical sections) of bacteria (red) and neutrophils (green). Scale bars, 25 μm. Insets are shown at higher magnification on the right panels for head and caudal regions. Scale bars, 10 μm. Neutrophils containing NADK knockdown bacteria can be seen in the caudal inset. (D) Representative fluorescence confocal images of transgenic mpx:GFP zebrafish larvae uninfected (CTRL), or intravenously injected with 104 S. aureus containing the empty vector (pSD1) or the NADK knockdown strain (NADK sgRNA) at 24 hpi, showing neutrophils (green). White arrows indicate the injection site. Scale bars, 500 μm (E) Number of neutrophils in uninfected zebrafish larvae (CTRL) or in zebrafish larvae intravenously injected with 104 S. aureus containing the empty vector (pSD1) or the NADK knockdown strain (NADK sgRNA) at 24 hpi. Comparison of data was performed using one-way analysis of variance (***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001).
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide kinase (NADK) promotes S. aureus virulence in zebrafish.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Elife