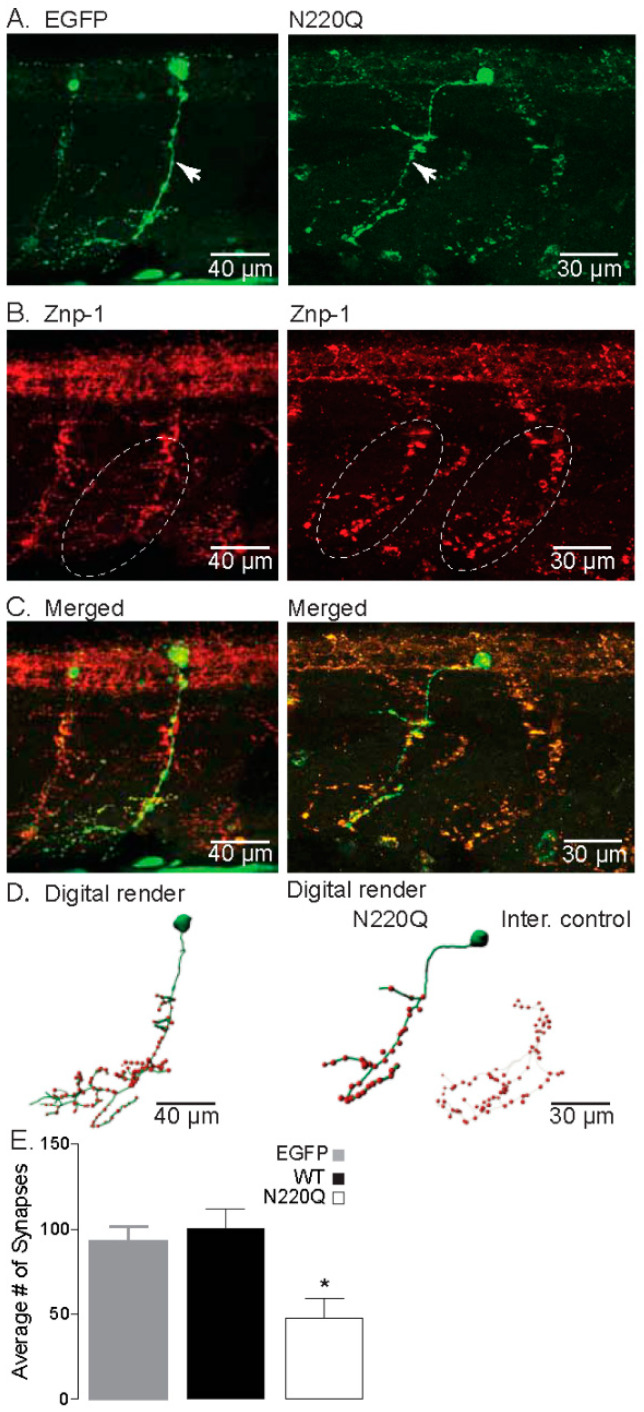
Figure 2 N-Glycosylation processing of the Kv3.1b protein impacts motor neuron development in zebrafish. (A) Confocal images of IHC staining of CaP neurons expressing either EGFP (left) or N220Q Kv3.1b (right) from 48 hpf embryos. Arrows denote main axonal branches. (B) Co-staining of Znp-1 highlights the extensive synapse points in the ventral myotome (dashed line oval). (C) Merged confocal projections from parts A and B, illustrating the lack of branches and lowered synapse numbers of CaP neurons expressing the N220Q Kv3.1b compared to EGFP alone or internal control. (D) Digital rendering of neuron morphology (green) and synaptic points (red) from part C, showing the extensive axonal branching of EGFP expressing neurons and internal control and high synaptic points compared to the CaP neuron expressing the N220Q Kv3.1b. (E) Average number of synapses of CaP neurons expressing EGFP (n = 10), WT (n = 8) and N220Q (n = 9) Kv3.1b proteins. Graphs denote mean ± SEM and were compared by Student’s t-test (* p < 0.0087). See also Movies Figures S4 and S5.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Biology (Basel)