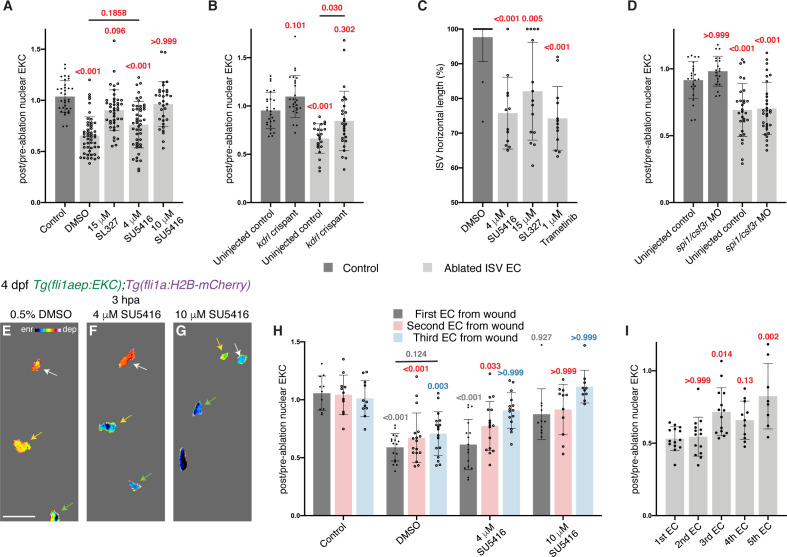
Figure 5 Erk activity in ablated vessels is maintained through the Vegfr pathway. (A) Ongoing Erk-signalling requires Vegfr and Mek activity. Quantification of post-/pre-ablation nuclear EKC intensity 3 hours post-ablation (hpa) in endothelial cells (ECs) of 0.5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-treated non-ablated control ISVs (33 ECs, n = 11 larvae) and ablated ISVs of larvae treated with either 0.5% DMSO (51 ECs, n = 17 larvae), 15 μM SL327 (42 ECs, n = 14 larvae), 4 μM SU5416 (47 ECs, n = 16 larvae), or 10 μM SU5416 (32 ECs, n = 11 larvae). (B) Kdrl is required for full induction of Erk activity in ablated ISV ECs. Quantification of post-/pre-ablation nuclear EKC intensity 3 hpa in non-ablated control ISV ECs of uninjected control (27 ECs, n = 9 larvae) and kdrl crispants (26 ECs, n = 9 larvae), and ablated ISV ECs of uninjected control (22 ECs, n = 8 larvae) and kdrl crispants (27 ECs, n = 9 larvae). (C) Quantification of ISV horizontal length (as percentage of control) for ablated ISVs in 24 hpa, 5 days post-fertilisation (dpf), EC-EKC larvae treated with either 0.5% DMSO (n = 18 larvae), 4 μM SU5416 (n = 12 larvae), 15 μM SL327 (n = 15 larvae), or 1 μM Trametinib (n = 13 larvae). (D) Macrophages are not required for maintaining Erk activity in ablated ISV ECs. Quantification of post-/pre-ablation nuclear EKC intensity 3 hpa in non-ablated control ISV ECs of uninjected control (24 ECs, n = 8 larvae) and spi1/csf3r morphants (21 ECs, n = 7 larvae), and ablated ISV ECs of uninjected control (29 ECs, n = 10 larvae) and spi1/csf3r morphants (31 ECs, n = 11 larvae). (E–G) Lateral spinning disc confocal images of ablated ISV ECs in 4 dpf, 3 hpa, EC-EKC larvae treated with either 0.5% DMSO (E), 4 μM SU5416 (F), or 10 μM SU5416 (G). EC Erk activity was consistently higher and more Vegfr-dependent closer to the wound. Arrows indicate first (white), second (yellow), and third (green) ECs from the wounded site. Full images: Figure 5—figure supplement 1D’,H’,J’. (H) Quantification of post-/pre-ablation nuclear EKC intensity at 3 hpa in first (dark grey), second (red), and third (light blue) ECs from wound. Treatments were 0.5% DMSO-treated non-ablated control ISVs (11 first, second, and third ECs, n = 11 larvae), and ablated ISVs of larvae treated with either 0.5% DMSO (17 first, second, and third ECs, n = 17 larvae), 4 μM SU5416 (16 first and second ECs, and 15 third ECs, n = 16 larvae), or 10 μM SU5416 (11 first and second ECs, and 10 third ECs, n = 11 larvae). The same embryos were used in (A). (I) Quantification of post-/pre-ablation nuclear EKC intensity at 3 hpa in first (14 ECs, n = 14 larvae), second (14 ECs, n = 14 larvae), third (14 ECs, n = 14 larvae), forth (11 ECs, n = 11 larvae), and fifth (8 ECs, n = 8 larvae) ECs from the wounded site of ablated ISVs in 4 dpf EC-EKC larvae. Data for the first, second, and third ECs were taken from Figure 4—figure supplement 1N. ISV: intersegmental vessel; DA: dorsal aorta. Statistical test: Kruskal-Wallis test was conducted for graphs (A, C, D, H, I). Ordinary one-way ANOVA test was conducted for graph (B). Error bars represent standard deviation. 15 μm for image (E).
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Elife