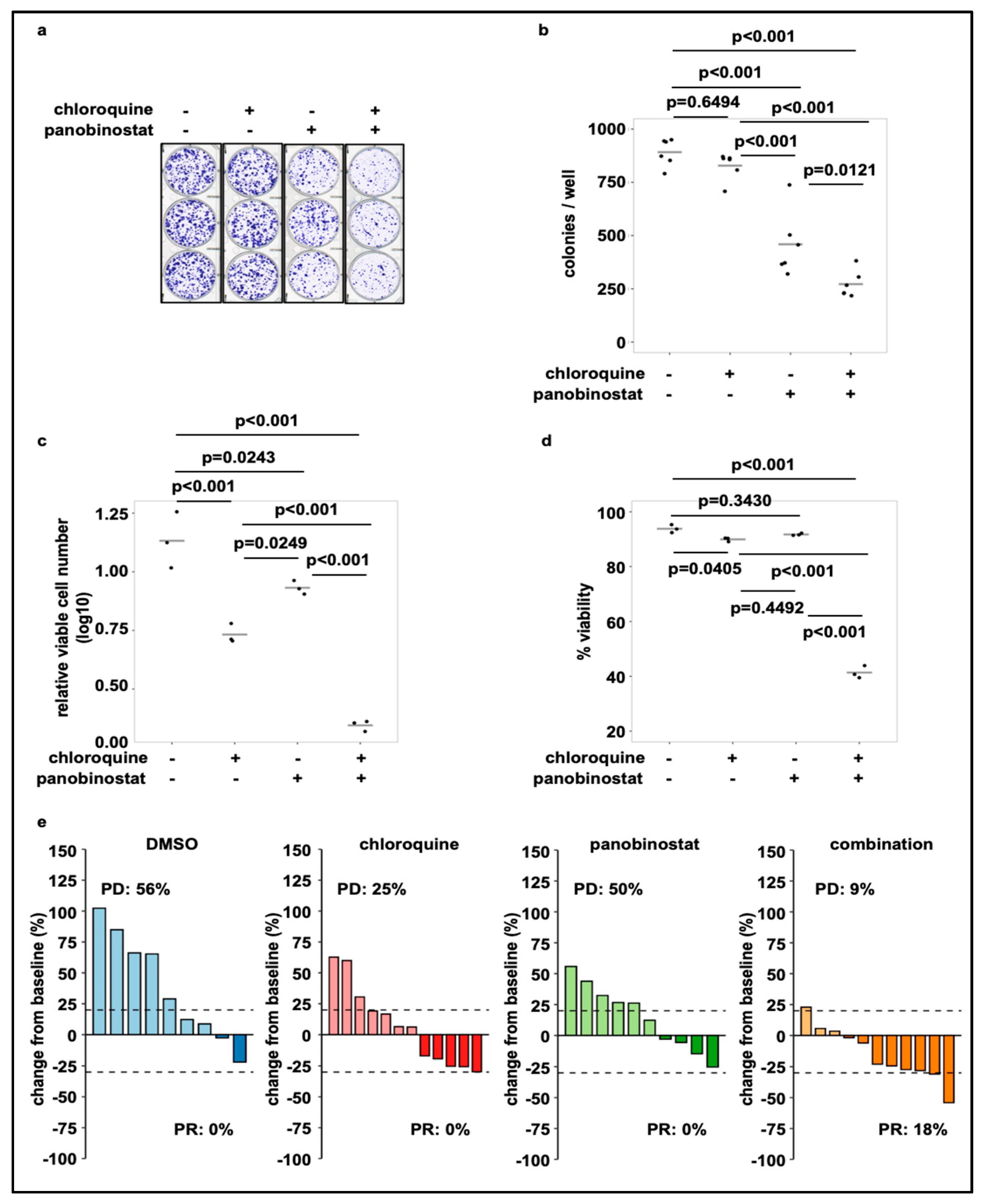
Fig. 5 Treatment with panobinostat in combination with chloroquine reduces cell viability and colony growth. (a) Colony formation assay of SK-N-BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cells treated for 24 h with chloroquine (20 µM) or panobinostat (10 nM) alone or in combination. Shown are 6 technical replicates from two independent experiments. (b) Quantification of grown colonies after treatment of SK-N-BE(2)-C cells for 24 h with chloroquine (20 µM) or panobinostat (10 nM) alone or in combination. (c) Viable cell number (normalized to DMSO) of SK-N-BE(2)-C cells after 72 h treatment with chloroquine (20 µM) or panobinostat (10 nM) alone and in combination. (d) Viability of SK-N-BE(2)-C cells after 72 h treatment with chloroquine (20 µM) or panobinostat (10 nM) alone and in combination. (b–d) Statistical analyses: ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (e) Waterfall plots demonstrating change in tumor volume (%) for each individual xenograft, from baseline (day 1 = start of the treatment) to day 3 after yolk sac-implantation of SK-N-BE(2)-C cells. Dotted lines are drawn according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) 1.1 adopted for zebrafish tumors, to visualize best response: progressive disease (PD), at least a 20% increase in tumor volume; partial response (PR), at least a 30% decrease in tumor volume; each bar reflects one individual xenograft. The following concentrations were applied: chloroquine: 100 µM; panobinostat: 200 nM.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Cells