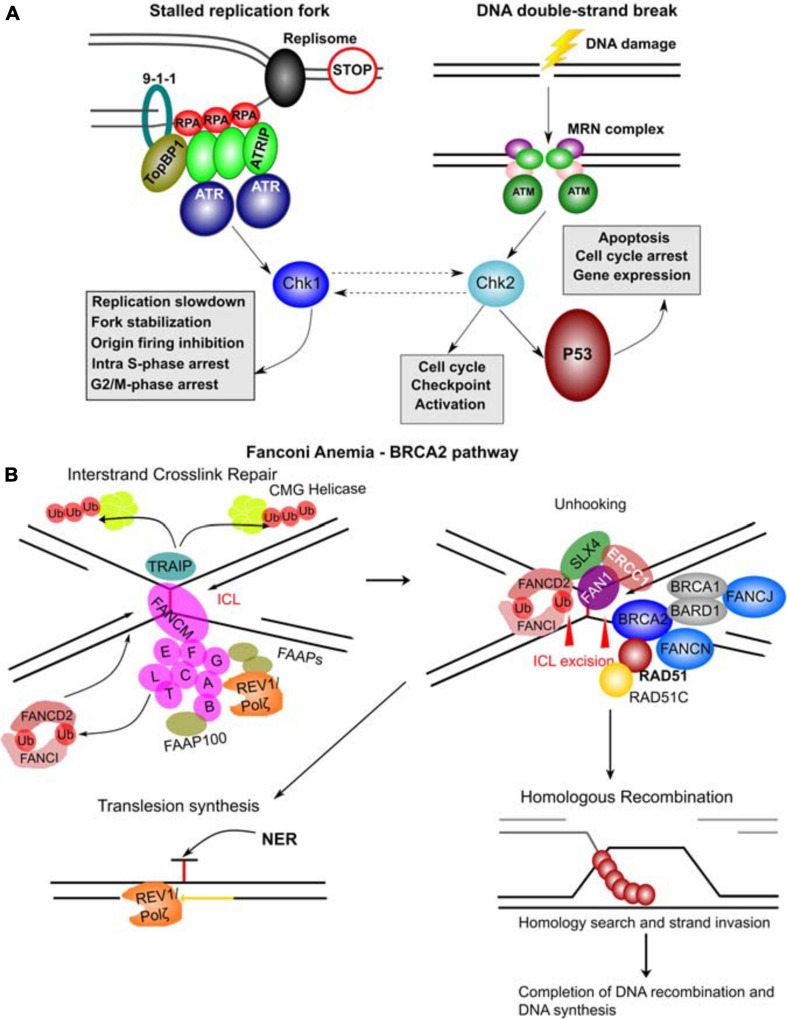
FIGURE 7 Molecular complexes formed and DNA repair pathways mediated by CPG proteins. (A) Mechanisms of ATR and ATM activation by different types of DNA damage. Stalled replication forks resulting from a blockage of replisome progression (indicated by the “STOP” diagram). The single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) region is recognized by Replication Protein A (RPA) forming the filaments which can then recruit ATR-ATRIP (ATR Interacting Protein) complexes. The RAD17-RFC complex (not shown) loads the 9-1-1 complex (RAD9-RAD1-HUS1) onto the ssDNA-dsDNA junction. RAD9 S387 phosphorylation provides a binding site for DNA topoisomerase 2-binding protein 1 (TopBP1), which in turn binds and activates ATR kinase. ATR phosphorylates and activates Chk1 kinase mediating many of its functional effects and directly phosphorylates many other target proteins. DNA double-strand breaks results in a complex signaling cascade resulting in binding of the MRN complex (MRE11-RAD50-NBN) to the DNA ends. MRN provides a DNA damage sensor platform for recruitment and activation of ATM, which then phosphorylates multiple targets including Chk2 responsible for cell cycle checkpoint activation and p53 activation. Chk2 and Chk1 can also functionally interact (hashed lines with arrows). p53 activation leads to apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and gene expression changes. (B) FA – BRCA2 pathway. A major role of this pathway is to respond to inter-strand crosslinks (ICL), which can be especially problematic during DNA replication since ICLs prevent replication fork convergence. At such blocked replication forks, TRAIP ubiquitin ligase ubiquitinates the CMG (CDC45-MCM-GINS) Helicase leading to its unloading. The ICL itself is recognized by FANCM / FAAP24 complex. FANCM then recruits the core FA complex components and FAAPs (FA associated proteins). E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme FANCT and E3 ubiquitin ligase FANCL then cooperate to perform mono-ubiquitination of FANCD2 and FANCI forming the ID2 complex. Monoubiquitinated ID2 complex gets recruited the ICL lesion. In the process of unhooking, DNA near the ICL gets processed by nucleases to enable specific DNA repair pathways. The strand with the ICL structure gets repaired by Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER) and the translesion synthesis by REV1/Polζ, which gets recruited by the FA core complex. ID2 recruits FANCP (SLX4), FANCQ (ERCC1) and the nuclease FAN1 to mediate the ICL incision. The ID2 also interacts with BRCA2 (FANCD1), which gets recruited to the parts of blocked replication forks that will have to go through DNA recombination. BRCA2 in complex with BRCA1, BARD1, FANCN, FANCJ, RAD51 and RAD51C as well as other factors leads to loading of RAD51 into resected ssDNA regions, which can then participate in homologous recombination (HR). The figure was constructed based on the information in several recent reviews (Awasthi et al., 2016; Fradet-Turcotte et al., 2016; Bonilla et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020).
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Front Cell Dev Biol