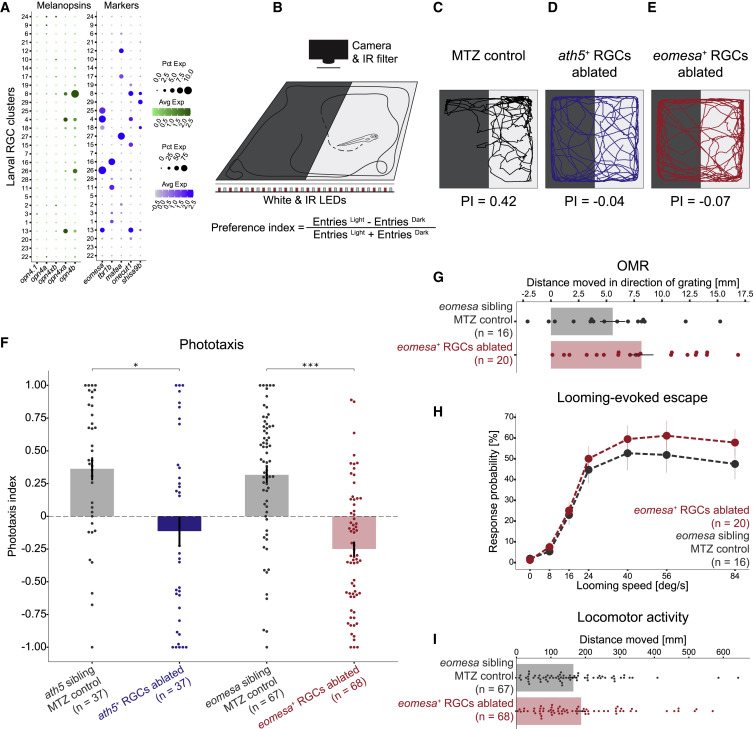
Fig. 7 (A) Dot plots showing type-specific expression of melanopsin in larval RGCs. Left: of five melanopsin homologs (columns), only opn4xa and opn4b have discernible expression in specific larval RGC clusters (rows). Right: opn4xa+ and opn4b+ clusters include eomesa+ RGC types, but not mafaa+ or tbr1b+ types. An opn+eomesa- RGC type is marked by the co-expression of onecut1 and shisa9b. Larval clusters are ordered as in Figure 3A. Expression patterns are conserved in adult RGC types (Figure S7D). (B) Phototaxis assay. Larvae are placed in a light-dark choice arena, and their positions are tracked over time. A phototaxis index (PI) quantifies attraction toward the light source. (C–E) Representative traces and PI values of an MTZ-treated control larva (C), ath5+ RGC-ablated blind larva (D), and eomesa+ RGC-ablated larva (E). (F) PI values for NTR- Tg(ath5:QF2) and Tg(eomesa:QF2) control siblings as well as ath5+ RGC ablated blind fish, and eomesa+ RGC-ablated larvae. Shown is a bar plot with a superimposed dot plot, where each dot represents one fish. Error bars represent SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Dunn post hoc test). (G) Quantification of optomotor response in MTZ-treated controls and eomesa+ RGC-ablated larvae, plotted as in (F). (H) Escape probability of MTZ-treated controls and eomesa+ RGC-ablated larvae to a looming disc. Each dot represents the mean value at a given stimulus expansion rate. Error bars represent SEM. (I) Quantification of locomotor activity of MTZ-treated controls and eomesa+ RGC-ablated larvae, plotted as in (F).
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Neuron