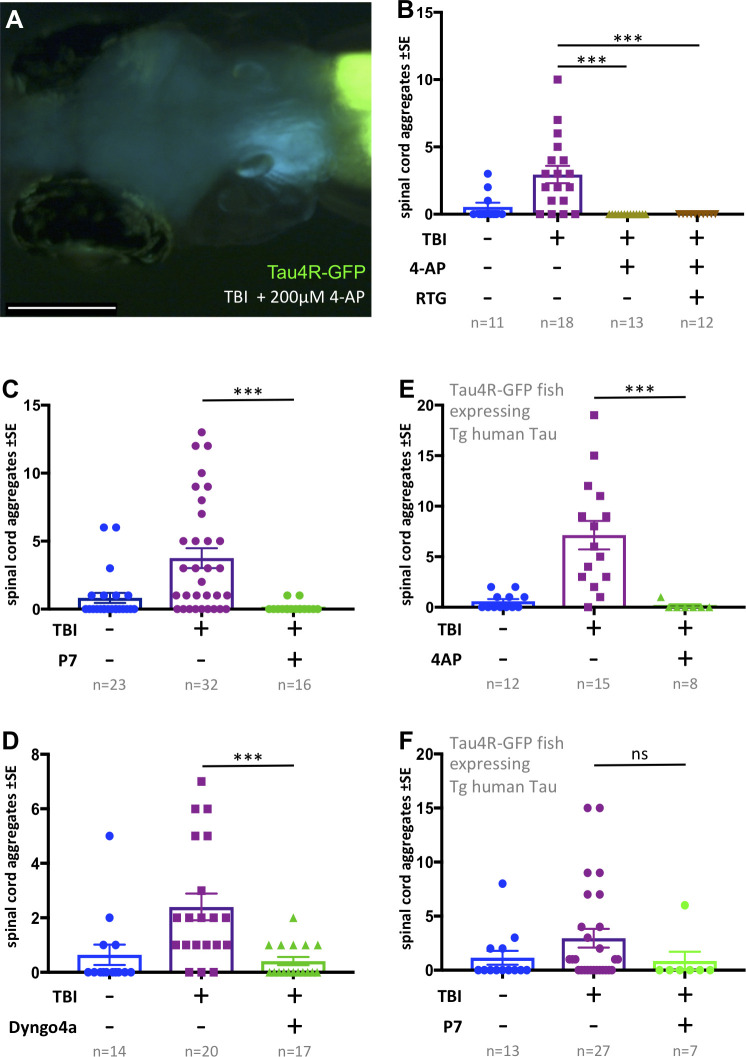
Figure 6 (A) Tau4R-GFP biosensor zebrafish larvae subjected to TBI and treated with the convulsant 4-AP show no brain puncta. Scale bar = 200 μm. (B) 4-AP significantly reduced (apparently eliminated) the abundance of GFP+ puncta in the brain and spinal cord compared to untreated TBI control. Results from alternative doses and timings of 4-AP are reported in Figure 6—figure supplement 1. The impact of 4-AP on tauopathy appears to be independent of its actions on post-traumatic seizures because reducing the latter with anti-convulsant retigabine (RTG) had no measurable effect. (C-F) Pharmacological inhibition of endocytosis reduced tauopathy following TBI. (C) Blocking endocytosis with Pyrimidyn-7 (P7) treatments significantly inhibited the formation of Tau4R-GFP+ puncta following TBI in zebrafish larvae (***p=0.001). (D) Dyngo 4a treatment significantly reduced Tau aggregates in the spinal cord (**p=0.0025) in a manner similar to P7. (E) 4-AP treatment significantly inhibited the formation of Tau4R-GFP+ puncta in the spinal cord (***p=0.0003) of Tau biosensor line that also express human Tau (0N4R) after traumatic brain injury compared to untreated TBI control group. (F) A notable reduction in Tau aggregates was observed in the same line after treatment with P7 drug. Statistical analysis shows no significance difference (ns, p=0.2223) between groups. n = number of larvae. ****p<0.0001, Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with Dunn’s multiple comparison test used throughout this Figure.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Elife