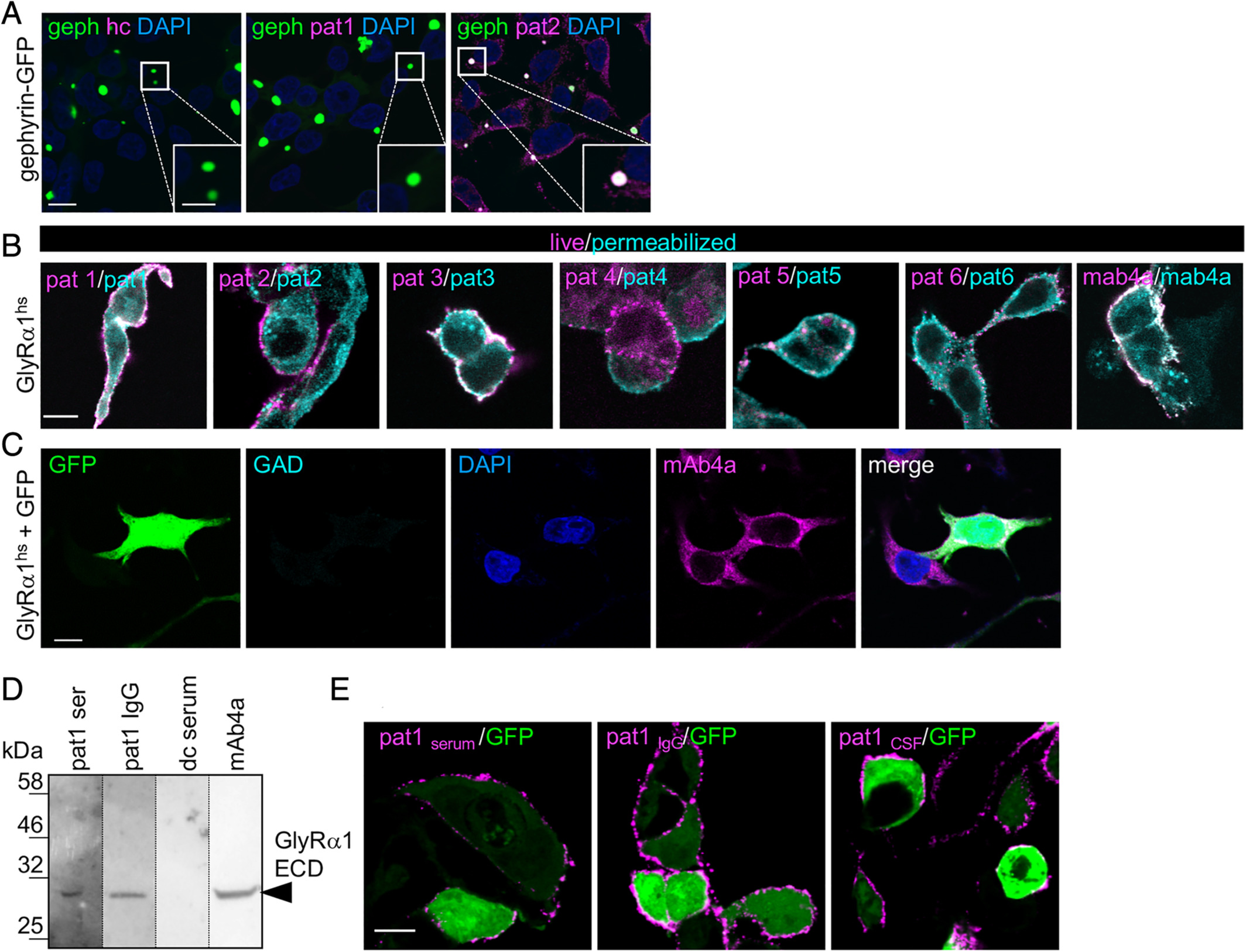
Fig. 6 Zebrafish larvae show abnormal escape response and reduced spinal cord GlyR cluster numbers upon treatment with patient serum. (A) Transfected HEK293 cells with various GlyR subunits of the zebrafish (dr = Danio rerio; α1, α2, α3, α4a, α4b, βa, βb) stained with serum of Patient 1 (pat1; magenta). Green fluorescent protein (GFP; green) was cotransfected. 4,6‐Diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI) was used to stain the nuclei. Note that pat1 serum specifically targets GlyR α2 and α4a (magenta). To some extent, α4b and βa were also stained. White bar = 20μm. (B, C) Sequence photographs of escape responses to tactile stimulation. The tip of the steel needle is visible in the bottom corner of each image. Touching the larva is indicated as 0 milliseconds. (B) Escape response of a healthy control (hc) serum permeated larva (n = 42). ACSF = artificial cerebrospinal fluid. (C) Escape response of a pat1 serum permeated larva (n = 29). This larva showed a weak convulsion in response to stimulation and remained stiff instead of initiating swimming. Scale bars = 1mm. (D, E) Stacked bar diagrams representing the different conditions of permeated larvae with patient serum or patient IgG. Black bars refer to portion of normal escape response (see also cyan dotted line for differences between conditions), gray bars refer to mild affected escape response, and red bars refer to severe impaired escape behavior (see also blue dotted line). All values are given as percentages. Animals analyzed for control conditions were ASCF, n = 38; hc, n = 42; glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)+, n = 34; pat1, n = 29; pat2, n = 29; pat3, n = 45; pat4, n = 32; pat1 IgG, n = 43; pat4 IgG, n = 36. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (F) Immunostaining of glycinergic synapses (GlyR green). Antisynapsin1 antibody was used as primary antibody to detect presynaptic terminals (magenta); NucRed is shown in blue. Boxed areas in F are enlarged at the top right corners of the images showing staining in close proximity to the nucleus. (G) Immunostaining of glutamatergic synapses. Antisynaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A (SV2) antibody was used as primary antibody to detect presynaptic terminals (magenta). α‐Amino‐3‐hydroxy‐5‐methyl‐4‐isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPARs) were stained with anti‐GluR2/3 antibody (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 5μm. (H, I) Relative number of GlyR clusters and AMPAR clusters following injection of the zebrafish with hc (blue) or pat1 serum (red) as compared to ACSF controls (black columns). **p < 0.01. ns = not significant.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Ann. Neurol.