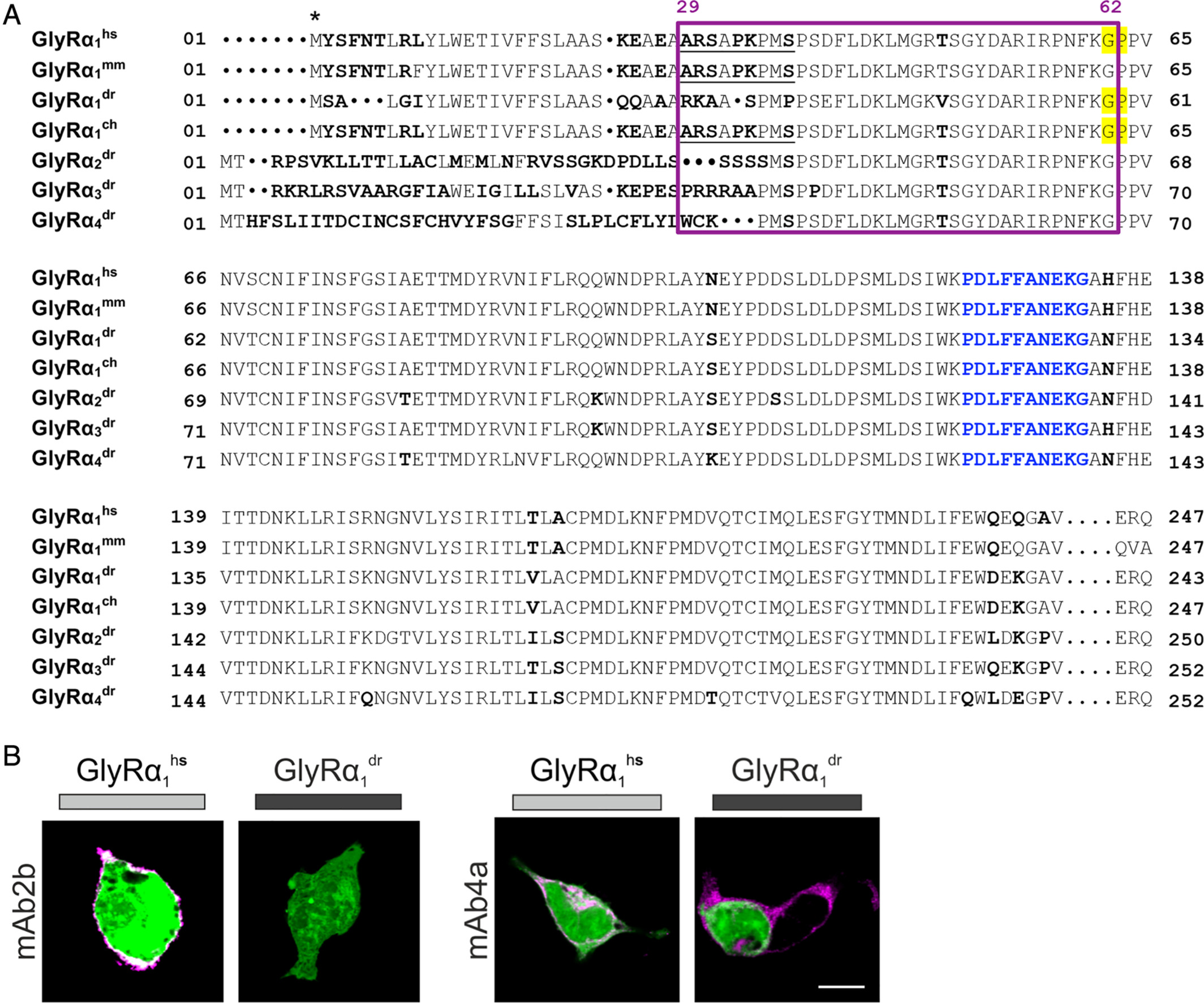
Fig. 4 The far GlyR N‐terminus determines species specificity of GlyR autoantibodies. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the extracellular domains of the immature GlyRα1hs, GlyRα1mm, GlyRα1dr, GlyRα1ch, GlyRα2dr, GlyRα3dr, and GlyRα4dr. Deviations in amino acid alignment are displayed in bold letters. The epitope of the monoclonal antibody mAb2b (α1‐specific antibody recognizing residues 1–10 of the mature protein) is underlined; the epitope of mAb4a pan‐GlyR antibody (present in GlyRα1dr; GlyRα1hs and GlyRα1ch residues 96–105) is marked by blue letters. Start of protein is marked by an asterisk (signal peptide first 28 residues). Residues that refer to the site of the restriction enzyme PpuM I used to generate a chimera are shaded in yellow. The proposed epitope of GlyR autoantibodies is marked by a pink box. (B) HEK293 cells where cotransfected with green fluorescent protein (green) and GlyRα1dr. The mAb2b antibody binds only to GlyRα1hs but not to GlyRα1dr, whereas the pan‐GlyR antibody mAb4a binds both the human and the zebrafish α1 subunit. White bar = 10μm. ch = chimeric; dr = Danio rerio; hs = Homo sapiens; mm = Mus musculus.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Ann. Neurol.