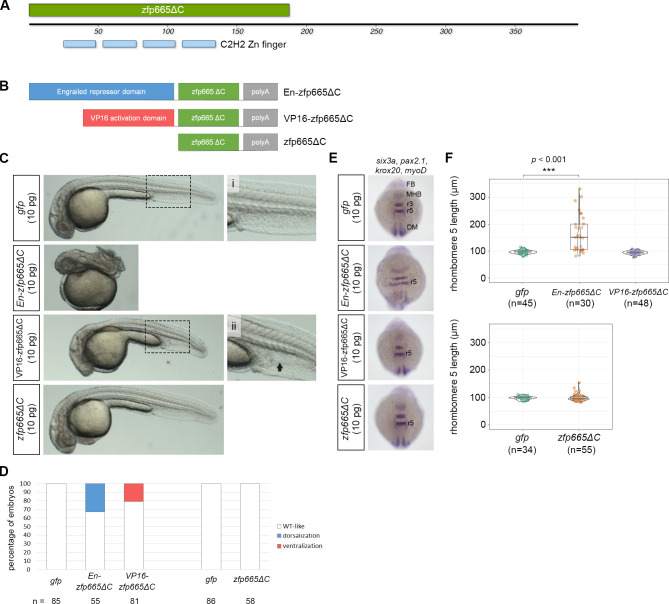
Fig 9
(A) A schematic representation of the protein domain organization of amphioxus zfp665, showing four consecutive C2H2-type zinc finger domains at the N-terminus. zfp665ΔC denotes the zinc finger region of zfp665 without its C-terminus. (B) A schematic representation of three different zfp665 fusion proteins, including engrailed repressor domain-zfp665ΔC fusion protein (En-zfp665ΔC), VP16 activation domain-zfp665ΔC (VP16-zfp665ΔC) fusion protein and the deletion of C-terminus of zfp665 (zfp665ΔC). (C) Phenotype of the zebrafish embryos injected with one of the three