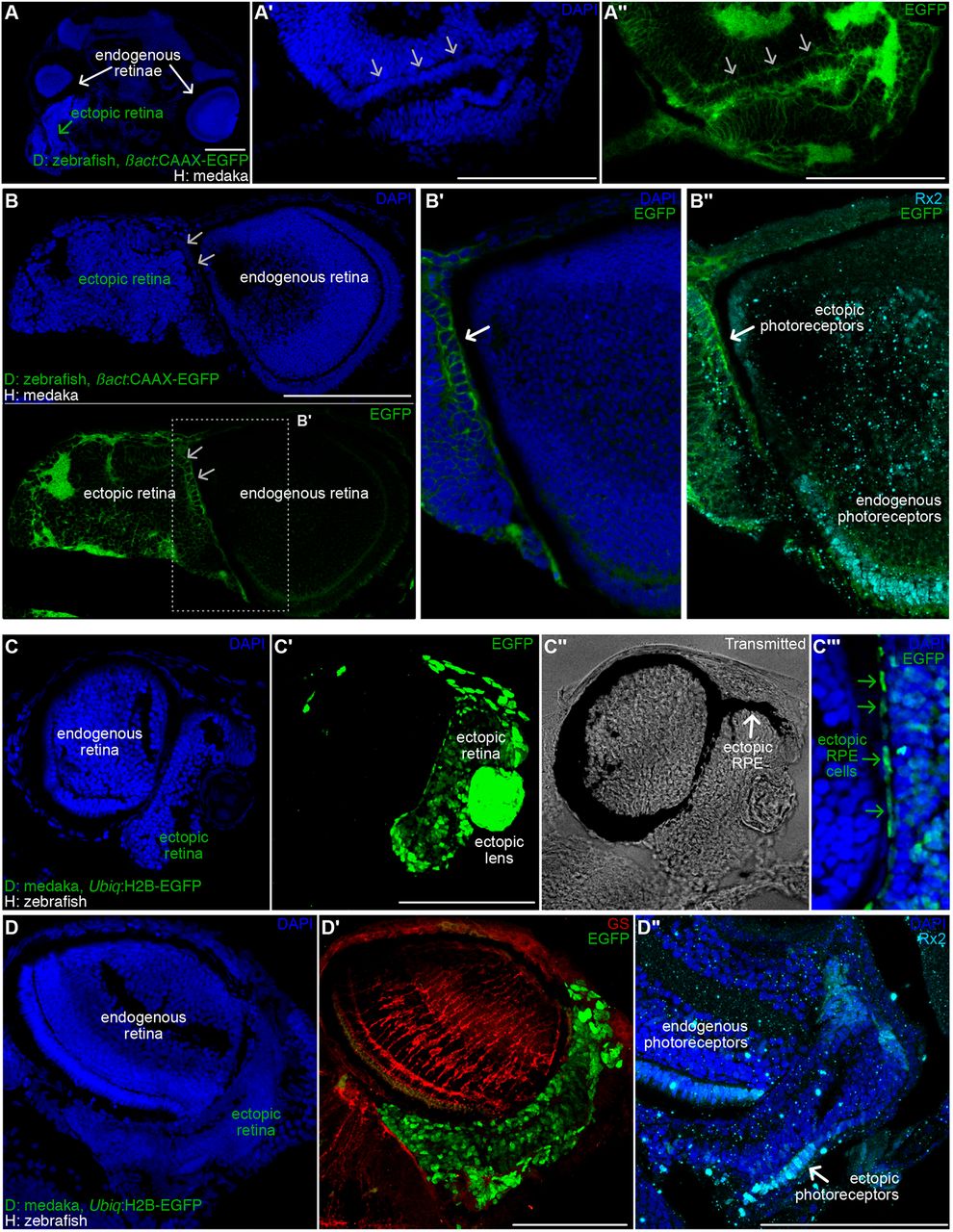
Fig. 5 Partial layering in the ectopic retinae of zebraka and medrafish. (A-B″) DAPI staining on cryosections of zebrakas using Tg(ßact:CAAX-EGFP) zebrafish as donors. (A) Cryosection of a transverse plane in a zebraka (dorsal is upwards, anterior is to the front) showing an ectopic retina (green arrow) ventrally adjacent to an endogenous retina (white arrow). Layering is evident in the ectopic retinae both by nuclear morphology (DAPI staining, arrows in A′ and B, top) and by membrane accumulation (CAAX-EGFP, arrows in A″, B, bottom, and B′) (n=6 ectopic retinae in 6 zebrakas). Immunostaining using anti-Rx2 Ab reveal photoreceptor identity of cells organised in layers (B″, white arrow) (n=3 zebrakas). (C-D″) DAPI staining (C,D) on cryosections of medrafish using Tg(Ubiq:H2B-EGFP) medaka as donors. (C′,D′) EGFP signal allows detecting ectopic cells. Transmitted channel (C″) analysis reveals ectopic RPE covering the dorsal part of the ectopic retina (arrow). Merged channels (C″) showing colocalisation of elongated EGFP+ nuclei and pigmented epithelium (green arrows). (D′) Immunostaining using an anti-GS antibody reveals Muller glia in the endogenous retina and not in the ectopic retina (n=4 medrafish). (D″) Immunostaining using an anti-Rx2 antibody label ectopic photoreceptors (arrow) organised in a mononuclear layer (n=3 medrafish). Scale bars: 100 µm. D, donor; H, host.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development