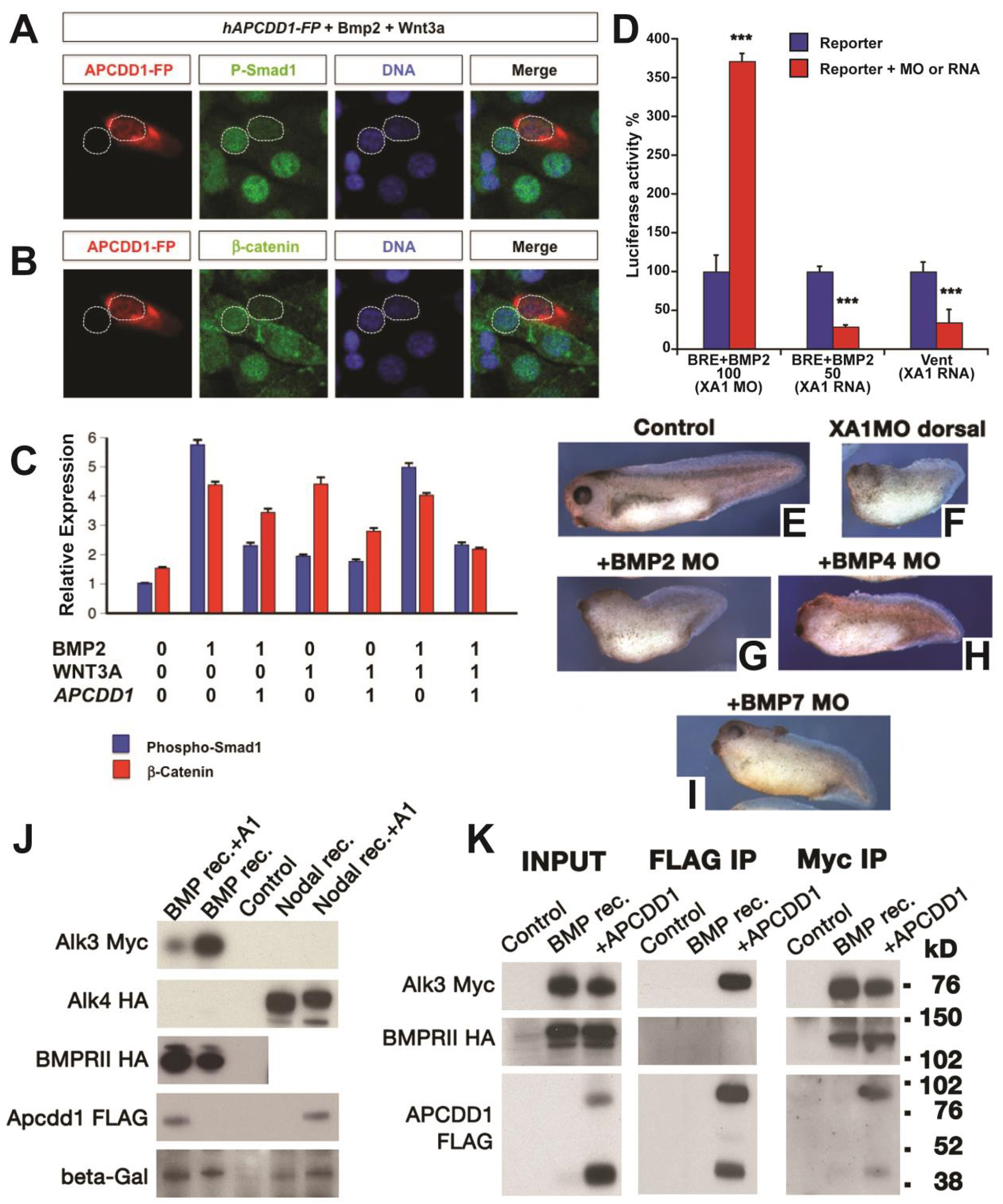
Fig. 3 APCDD1 inhibits BMP signaling in cells and tissues. A-B. The activation of BMP and Wnt pathways was measured at single-cell level, using NIH 3T3 mouse fibroblast cells cultured in the presence of BMP and Wnt ligands. Cells transfected with human APCDD1 and a fluorescence reporter (displayed in red) have low levels of both pSmad1 (green in A) and β-catenin (green in B), while neighboring cells that are not transfected have higher levels of both effectors. Nuclei are visualized with DAPI (blue). C. The immunofluorescence levels of pSmad1 and β-catenin were measured relative to the background (relative expression, Y axis), in the presence (0) or absence (1) of one or both ligands (Bmp2, Wnt3A) or of APCDD1 (n = 40 cells per condition). The outputs of BMP and Wnt signaling are inhibited by APCDD1 (p < 0.001 in Bonferroni-adjusted 2-way heteroscedastic t-test comparisons). D. Effect of Xenopus Apcdd1 (XA1) modulation on BMP-induced transcriptional activity in Xenopus animal injections. Apcdd1 depletion increases transcription induced by exogenous BMP2 RNA, while overexpression of apcdd1 RNA reduces transcription from both the BRE reporter induced by exogenous BMP2, and of the Vent promoter induced by endogenous BMP ligands. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 in Student’s t-test. Embryos were collected at stage 10.5, four embryos per assay, in triplicate, and each experiment was repeated a minimum of 3 times. E-I. The phenotype of XA1 depletion on the dorsal side is rescued most effectively by simultaneous BMP7 depletion (quantification in Fig. S1E). Embryos injected at the 4-cell stage on the dorsal side were collected at stage 36. The dorso-anterior index (DAI) values (Kao and Elinson, 1988) are: E – DAI5 (normal), F – DAI2, G – DAI2, H – DAI3, I – DAI4. For D-I, at least 10 Xenopus embryos, in three different experiments, were examined for each time point and experimental condition. J. Human APCDD1 specifically reduces the protein level of type I BMP receptor BMPRIA, but not the type II receptor BMPR2 and nodal type I receptor ACVR1B. Beta-galactosidase serves as loading control. Xenopus embryos were injected in the animal poles. K. APCDD1 interacts directly with BMPRIA, but not with BMPR2, in CHO cells. APCDD1 and BMPRIA coprecipitated in both APCDD1 (center panel) and BMPRIA (right panel) immunoprecipitation. BMPR2 coprecipitated with BMPRIA (right panel), but not with APCDD1 (center panel).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 464(1), Vonica, A., Bhat, N., Phan, K., Guo, J., Iancu, L., Weber, J.A., Karger, A., Cain, J.W., Wang, E.C.E., DeStefano, G.M., O'Donnell-Luria, A.H., Christiano, A.M., Riley, B., Butler, S.J., Luria, V., Apcdd1 is a dual BMP/Wnt inhibitor in the developing nervous system and skin, 71-87, Copyright (2020) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.