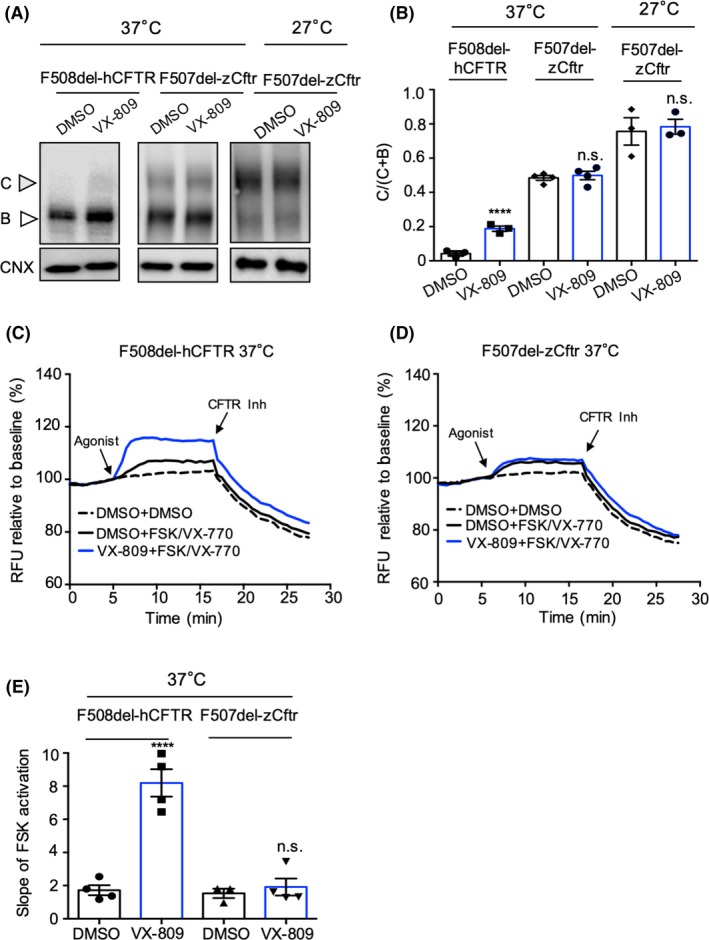
Figure 5
At 37°C, zebrafish Cftr (F507del) exhibits negligible rescue of the processing defect with VX‐809. A, HEK cells were transiently transfected with F508del‐hCFTR‐GFP (left) and F507del‐zCftr‐GFP (right two panels), in the presence or absence of 3 μM VX‐809 at 37 or 27°C. Band C, fully processed, mature complex‐glycosylated CFTR; Band B, immature core‐glycosylated CFTR are indicated. Unlike the human mutant, there is no positive effect of VX‐809 on processing of the zebrafish mutant. B, Bar graphs show the quantification of immunoblots like those shown in A) for four biological repeats. The bars show mean (±SEM) of the ratio C/(C + B) for the human and zebrafish mutants. C, Representative traces (membrane depolarization assay) for F508del‐hCFTR‐GFP channel activation and potentiation, with or without VX‐809 pretreatment. In these experiments, CFTR‐mediated depolarization was inhibited with the addition of CFTRinh‐172 (10 µM). D, Unlike the human mutant, there is no effect of VX‐809 on activated and potentiated F507del‐zCftr‐GFP channel function following chronic treatment with 3 μM VX‐809. E, Bar graph shows the mean (±SEM) of the initial slope after potentiation at 37°C (n = 4). Calnexin (CNX) was used as a loading control. (**