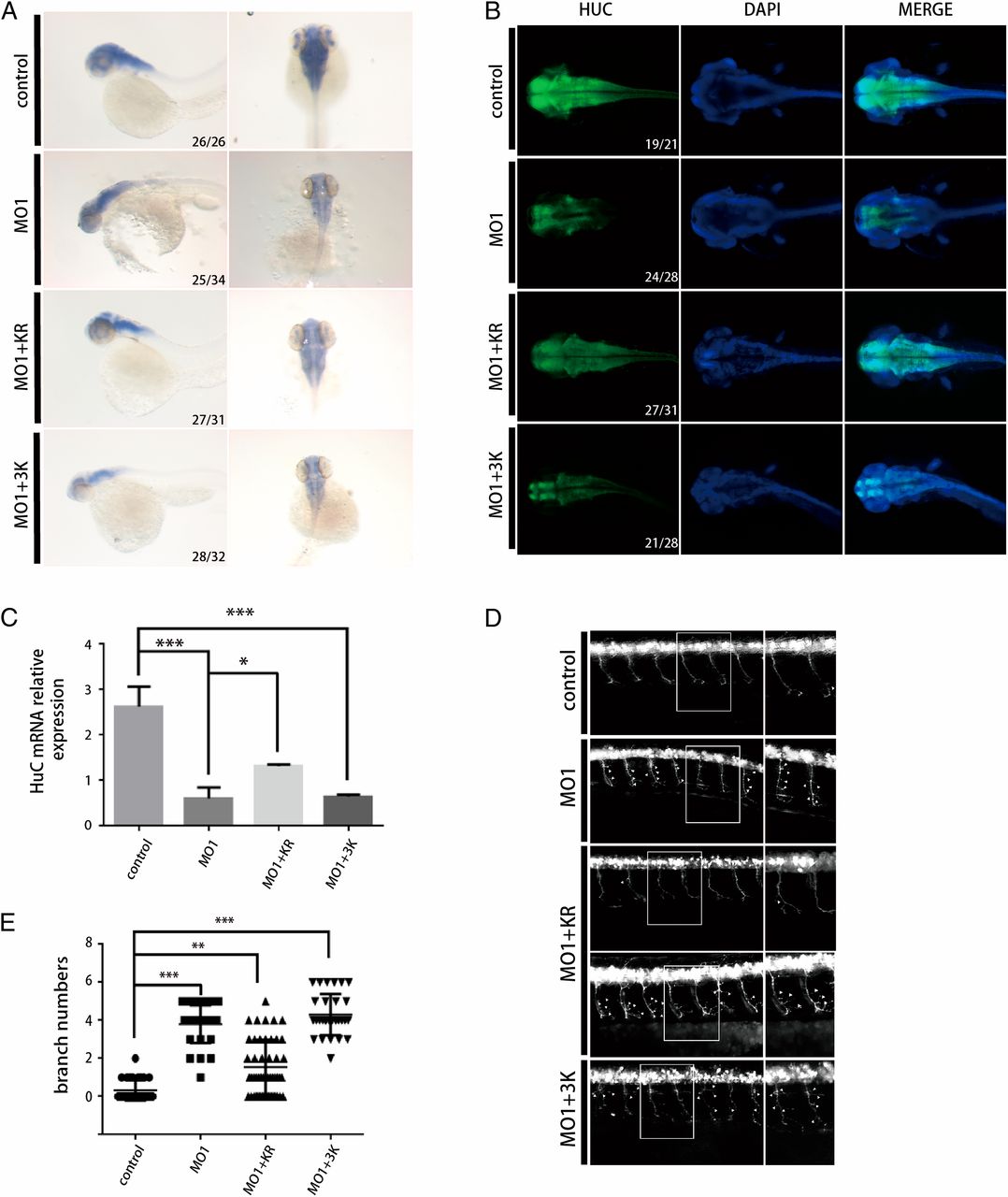
Fig. 6
Mutations of TBC1D23 in phosphoinositide- and FAM21-binding sites lead to abnormal motor neuronal development in zebrafish. (A) Expression of HuC (elavl3) in zebrafish at 48 hpf; control, control MO injection; MO1, MO1 injection; MO1+KR, MO1 and TBC1D23 K585D/R606D (KR) mutant mRNA coinjection; MO1+3K, MO1 and TBC1D23 K632E/K633E/K634E (3K) mutant mRNA coinjection. All injections are performed at one-cell stage of the development. (Left) Lateral view; (Right) dorsal view. (B) Whole-mount immunofluorescent staining of HuC (green) and DAPI (blue) showing the effects of the KR and 3K mutants. Dorsal views are shown. (C) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the transcription level of HuC. Mean ± SEM; n = 3; ***P < 0.001; *P < 0.05. (D) Morphology of CaP axons from embryos at 48 hpf that were injected MO1 and/or different mRNA. All injections were performed at one-cell stage of the Tg [hb9: GFP]ml2 transgenic zebrafish embryos. Arrows indicate abnormal branches. (Left) Lateral views and (Right) enlarged views of rectangles at Left. (E) Statistical results of the branch number of CaP axons in embryos treated as in D. For the KO1+KR group, 48 axons from 10 different Tg [hb9: GFP]ml2 transgenic zebrafish embryos were used for analysis; for the rest of the groups, 30 axons from 6 embryos were used. ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01.