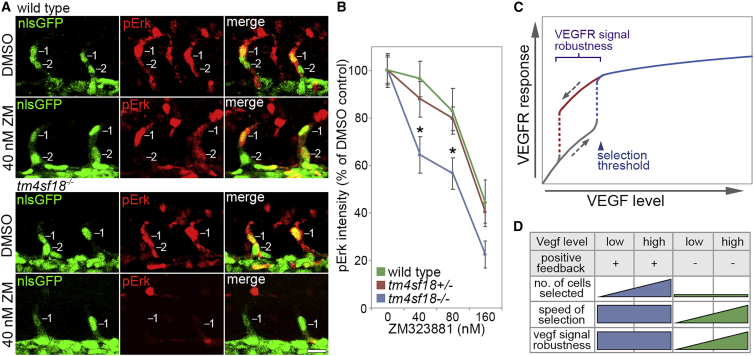
Figure 7
Robustness of Tip Identity Is Lost in
(A) Lateral views of sprouting ECs in ISVs of WT and
(B) Quantification of pErk fluorescence intensity in WT,
(C) Putative role of positive-feedback-generated bistability and hysteretic dynamics in the control of VEGFR signal level robustness in angiogenesis. Bistability ensures that higher levels of VEGF are required to induce tip patterning than to reverse this active state, conferring robustness on tip identity against fluctuations in VEGF levels.
(D) Impact of Tm4sf18-mediated positive feedback on the magnitude, speed, and robustness of motile EC selection during ISV branching. Tm4sf18 drives quick and robust decision making but also ensures delicate modulation of the magnitude of EC selection by Vegf levels. In the absence of Tm4sf18, the magnitude of EC selection is diminished, and both the speed and robustness of EC selection are highly variable and more dependent on Vegf level.
Data are means ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA or two-tailed t test. Scale bar, 25 μm.