Fig. 3
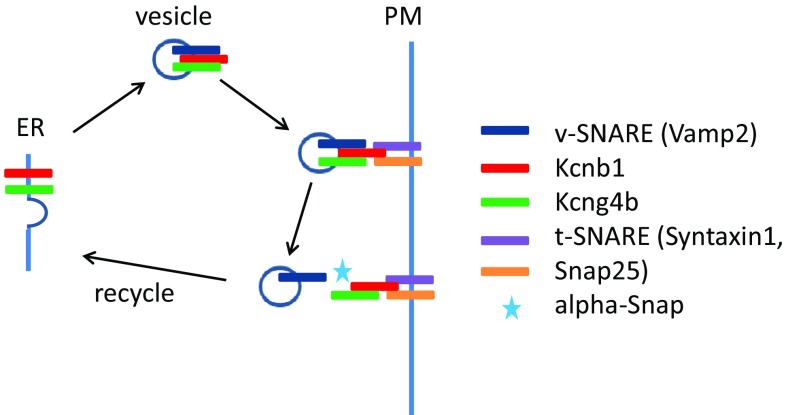
Genetic analyses reveal a role of the Kcnb1-Kcng4 axis in development of the BVS. Mutation/LOF of Kcg4b causes strong hydrocephalus and GOF—almost complete failure of ventricle inflation. In contrast, Kcnb1 mutant shows the slit-ventricle phenotype. The defect of Kcnb1 not only eliminates function of this protein as an electrically active subunit of voltage-gated Kv channel. Given its role in transport of Kcng4b, the defect of Kcnb1 negatively impacts function of both proteins, which counteract each other activity at the plasma membrane. Thus, the complete LOF of Kcnb1 could be partially compensated by a deficiency of Kcng4b transport. Note that Kcng4b is not expressed in adult animals suggesting that its modulation of Kcnb1 activity takes place only during development