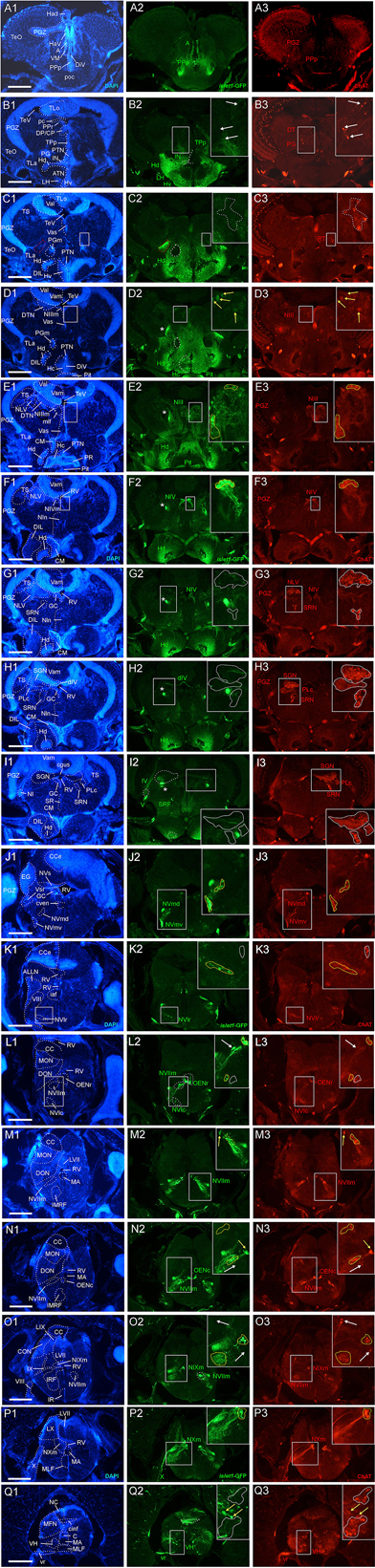
Fig. 2
Analysis of islet1-GFP expression in the adult zebrafish brain using a rostrocaudal series of sections showing also fluorescent DAPI stain and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) immunohistochemistry from olfactory bulb (A) to spinal cord (Q). The left column (A1–Q1) presents a general neuroanatomical analysis performed on the nuclear stain DAPI. In the middle column (A2–Q2), only brain nuclei containing islet1-GFP cell bodies and motor cranial nerves, but not other stained fibers, are identified in green lettering. In the right column (A3–Q3) only brain nuclei containing ChAT positive cell bodies and some motor nerve fibers are identified in red lettering. White arrows/fine stippled lines point to/encircle single labeled cell bodies/cell populations, whereas yellow arrows/fine stippled lines point to/encircle double-labeled cell bodies/cell populations. Occasionally, selected structures pointed out in DAPI stains with coarse stippled lines are also indicated in the islet1-GFP and ChAT pictures to ease identification. A conspicuous islet1-GFP positive tract is present from the level of the medial preglomerular nucleus where it is encircled with a red coarse stippled line (C1,C2) and then identified with an asterisk into the isthmic level (D2–I2). #: indicates in (D3–H3) a ChAT positive fiber net (see Mueller et al., 2004). A, anterior thalamic nucleus; ac, anterior commissure; ALLN, anterior lateral line nerve; AP, area postrema; ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; C, central canal; CC, crista cerebellaris; CCe, corpus cerebelli; cgus, commissure of secondary gustatory nuclei; cinf, commissura infima of Haller; CM, corpus mamillare; CON, caudal octavolateralis nucleus; CP, central posterior thalamic nucleus; cven, ventral rhombencephalic commissure; DAO, dorsal accessory optic nucleus; Dc, central zone of dorsal telencephalon; dIV, decussation of trochlear nerve; DIL, diffuse nucleus of inferior lobe; DiV, diencephalic ventricle; Dl, lateral zone of dorsal telencephalon; Dm, medial zone of dorsal telencephalon; DON, descending octaval nucleus; DP, dorsal posterior thalamic nucleus; Dp, posterior zone of dorsal telencephalon; DS, saccus dorsalis; DT, dorsal thalamus; DTN, dorsal tegmental nucleus; EG, eminentia granularis; End/ENv, dorsal/ventral entopeduncular nucleus; fr, fasciculus retroflexus; GC, griseum centrale; gl, glomerular layer (olfactory bulb); Had/Hav, dorsal/ventral habenular nucleus; Hc/Hd/Hv, caudal/dorsal/ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; iaf, internal arcuate fibers; icl, inner granular cell layer (olfactory bulb); IMRF, intermediate reticular formation; IN, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus; IO, inferior olive; IR, inferior raphe; IRF, inferior reticular formation; LIX, lobus glossopharyngeus; LVII, lobus facialis; LX, lobus vagus; LC, locus coeruleus; lfb, lateral forebrain bundle; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; MA, Mauthner axon; mfb, medial forebrain bundle; MFN, medial funicular nucleus; mlf, medial longitudinal fascicle; MON, medial octavolateralis nucleus; NIII, oculomotor nerve nucleus; NIV, trochlear motor nerve nucleus; NIXm, glossopharyngeal motor nerve nucleus; NVmd, dorsal trigeminal motor nerve nucleus; NVmv, ventral trigeminal motor nerve nucleus; NVs, primary sensory trigeminal nucleus; NVIc/NVIr, caudal/rostral abducens motor nerve nucleus; NVIImc/NVIImr, caudal/rostral facial motor nerve nucleus; NXm, vagal motor nerve nucleus; pc, posterior commissure; NI, nucleus isthmi; NIn, Nucleus interpeduncularis; NLV, nucleus lateralis valvulae; OB, olfactory bulb; OENc/OENr, caudal/rostral octavolateralis efferent neurons; P, pallium; pc, posterior commissure; PG, preglomerular complex; PGm, medial preglomerular nucleus; PGZ, periventricular gray zone of optic tectum; Pit, pituitary; PLc, caudal perilemniscal nucleus; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; poc, postoptic commissure; PPa/PPp, anterior/posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PPr, periventricular pretectum; PR, posterior hypothalamic recess; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; RT, rostral tegmental nucleus (of Grover and Sharma, 1981); RV, rhombencephalic ventricle; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; SD, subpallial dopaminergic cells; SGN, secondary gustatory nucleus; SGT, secondary gustatory tract; SP, subpallium; SPr, superficial pretectum; SO, spino-occipital region; SR, superior raphe; SRF, superior reticular formation; SRN, superior reticular nucleus; TelV, telencephalic ventricle; TeO, optic tectum; TeV, tectal ventricle; TLa, torus lateralis; TLo, torus longitudinalis; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; TPp-p, parvocellular cell part of TPp; TPp-m, magnocellular (pear-shaped) cell part of TPp; TS, torus semicircularis; ttb, tractus tecto-bulbaris; Val, lateral part of valvula cerebelli; Vam, medial part of valvula cerebelli; Vas, vascular lacuna; Vdd/Vdv, dorsal/ventral subnucleus of dorsal nucleus of ventral telencephalon; VG, vagal group of catecholamine neurons; VH, ventral horn; VL/VM, ventrolatateral/ventromedial thalamic nucleus; vot, ventrolateral optic tract; Vp/Vs/Vv, posterior/supracommissural/ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalon; vr, ventral spinal root; Vsr, sensory trigeminal root; IV/V/VIII/IX/X, trochlear, trigeminal, octaval, glossopharyngeal, vagal nerve (motor components).