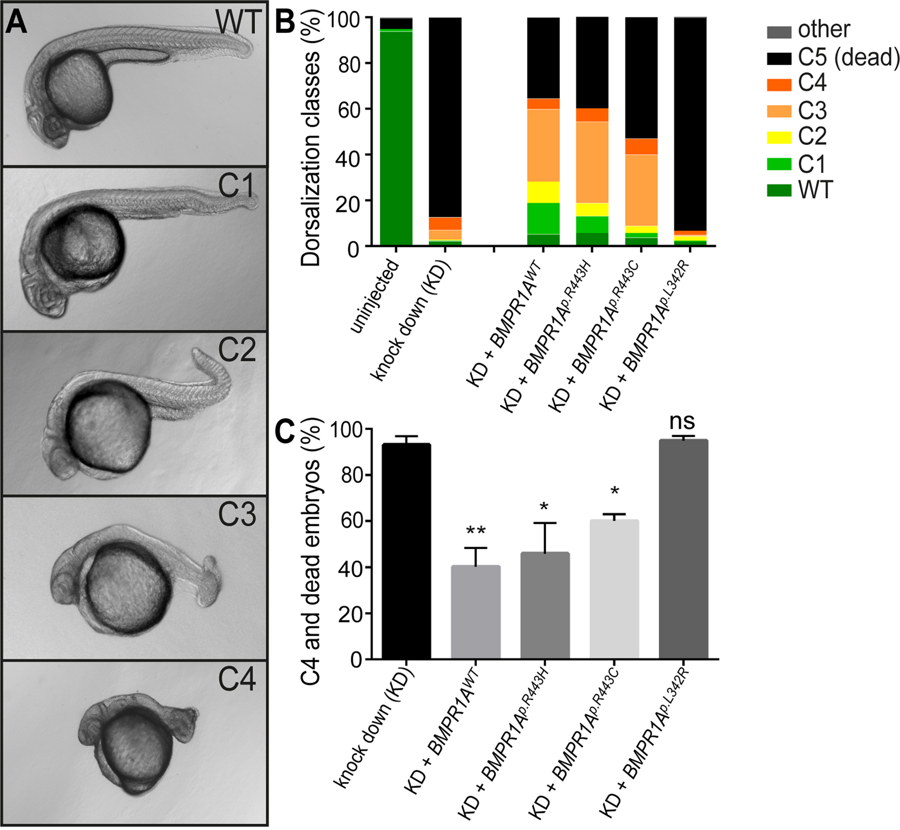
Fig. 3
Rescue of bmpr1aa morphant dorsalization phenotypes in zebrafish by injection of mRNA encoding human BMPR1A. (A) Representative classes of dorsalization phenotypes in zebrafish embryos at 24hpf as previously described36. (B) Mean percentages of the five dorsalization classes among the different experimental groups [total number of embryos analysed: uninjected, n = 528; bmpr1aa MO knockdown (KD), n = 217; KD + BMPR1AWT mRNA, n = 228; KD + BMPR1Ap.R443H mRNA, n = 255; KD + BMPR1Ap.R443C mRNA (JPS), n = 147; KD + BMPR1Ap.L342R mRNA (Linkspoot), n = 219]. (C) Share of embryos with C4 phenotype or lethality (mean ± SEM) after knockdown and human BMPR1A mRNA rescue injections by 24hpf [Total number of injected embryos: n = 1066 (Supplementary Tables S6, S7, S8, S9, S10). Number of experiments: KD, n = 5; KD + BMPR1AWT mRNA, n = 6; KD + BMPR1Ap.R443H mRNA, n = 5; KD + BMPR1Ap.R443C mRNA (JPS), n = 4; KD + BMPR1Ap.L342R mRNA (Linkspoot), n = 4. Indicated is the statistical significance of the difference between the occurrence of severe dorzalisation defects in each condition compared with the pure knockdown (KD) (*p’ < 0.05, **p’ < 0.01, ns: not significant)].