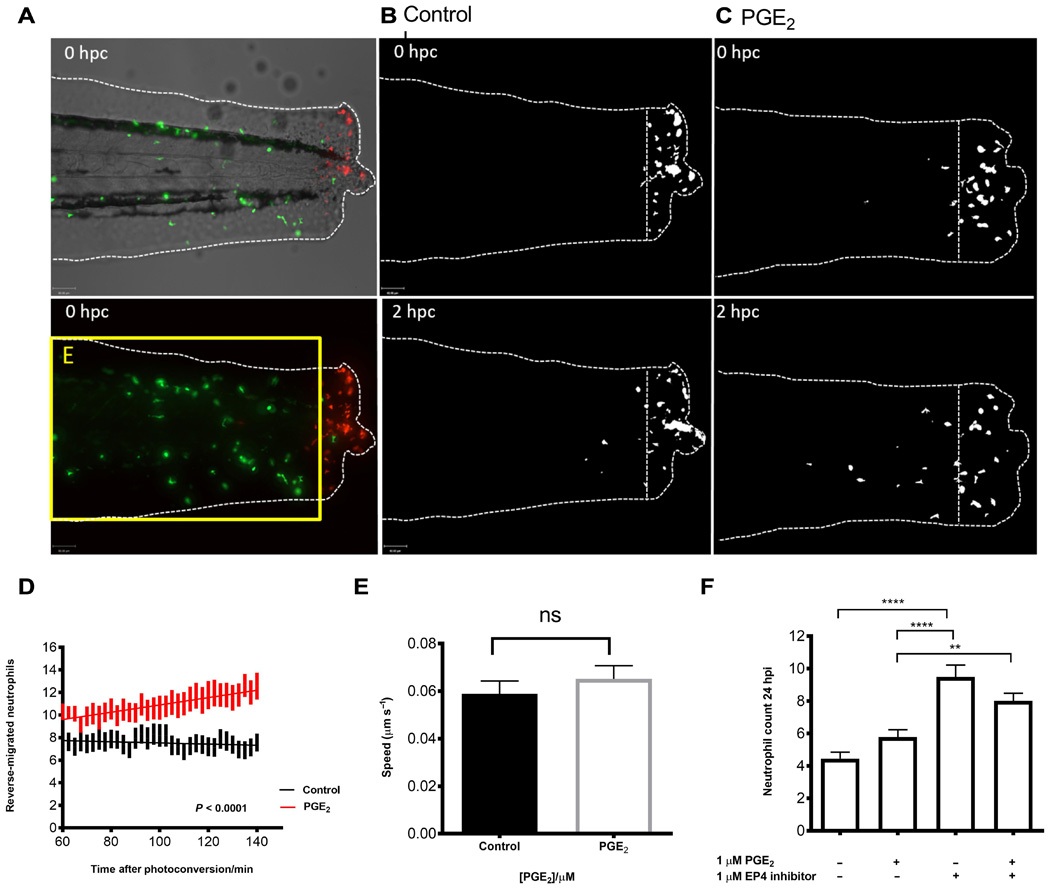
Fig. 4
PGE2 drives accelerated reverse migration through EP4 receptor signaling.
(A) Representative photomicrographs of control or PGE2-treated 3 dpf Tg(mpx:gal4)sh267;Tg(UAS:kaede)i222 larvae following photoconversion. The area to the right of the white dashed vertical line indicates wound site, where cells were photoconverted from green to red fluorescence. The yellow box E indicates the area into which the photoconverted cells migrate and corresponds to data in (D). (B) The red channel only is shown as a binary image of a control larva at 0 and 2 hours post conversion (hpc). Very little migration away from the wound site occurs between 10 and 12 hpi. (C) Binary images of the red channel of a PGE2-treated larva at 0 and 2 hpc. At 12 hpi, neutrophils have migrated away from the wound site, when treated with PGE2. (D) Plot showing the number of neutrophils moving away from the wound over 10 to 12 hpi, preincubated with or without PGE2 from 8 to 9 hpi. PGE2-treated neutrophils migrate away from the site of injury between 10 and 12 hpi more readily. Line of best fit shown is calculated by linear regression. P value shown is for the difference between the two slopes. (E) The speed of neutrophils moving away from the site of injury is not significantly different in the presence of exogenous PGE2, indicating that neutrophils migrate away sooner rather than at a greater speed in PGE2-treated larvae. (F) Neutrophil counts at 24 hpi show a significant increase in neutrophil number when EP4 signaling is blocked using the antagonist AH23848 **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. Addition of PGE2 does not lead to significant abrogation of this effect, implying PGE2 signals through the EP4 receptor to promote neutrophil removal. All data are presented as means ± SEM, from n = 18 larvae for (D) and (E) and n = 53 for (F) from three experimental repeats. Images were taken using ×10 magnification on a TE2000U inverted microscope (Nikon).