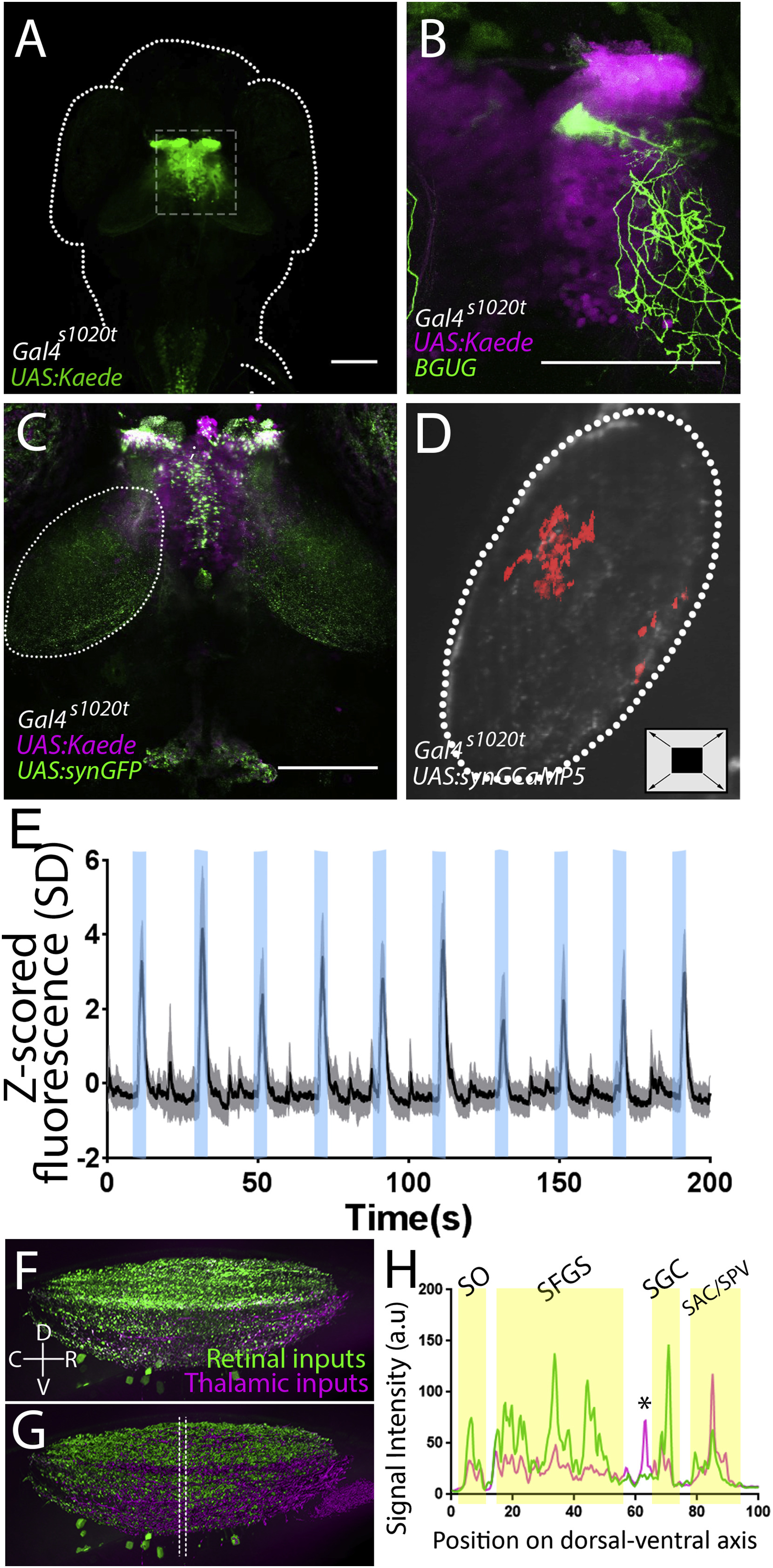
Fig. 2
Thalamic Projection Neurons Deliver Loom Information to the Tectum
(A) Strong Kaede expression is present in the thalamus of a Gal4s1020t; UAS:Kaede larva (a z series of this expression pattern can be found in Video S2).
(B) An individual thalamic projection neuron, revealed using the Brn3c:Gal4;UAS:GFP transgene (Scott et al., 2007), ramifies broadly in the tectal neuropil (a 3D rotation of this cell can be found in Video S3).
(C) Expressing a synaptically targeted GFP under the control of Gal4s1020, we see presynaptic terminals of thalamic projection neurons in the tectal neuropil (white outline; a z series is shown in Video S4).
(D) By expressing GCaMP in these terminals (in Gal4s1020;UAS:synGCaMP5g larvae), we can gauge when communication is taking place. The location of the presynaptic activity of thalamic axons in the tectal neuropil during looming stimuli in these animals is shaded red.
(E) Activity in these synaptic terminals during ten looming stimuli (shaded in blue) across all animals (shading indicates S.D., n = 5).
(F) A z projection of the tectal neuropil, rotated perpendicular to the field of view. Green indicates RGC axons, and magenta shows thalamic projection neurons.
(G and H) Imaris rendering of (F) (an animation of this rendering can be found in Video S5). The space between the lines in (G) indicates the area sampled to produce a dorsal-ventral map (H) of thalamic projections registered against those from the retina. RGC-defined laminae are indicated with yellow shading, and a thalamo-recipient lamina between the SFGS and SGC is indicated by an asterisk. SO, stratum opticum; SFGS, stratum fibrosum et griseum superficiale; SGC, stratum griseum centrale; SAC/SPV: stratum album centrale and stratum griseum periventriculare. Scale bars indicate 100 μm.