Fig. 5
Fig. 5
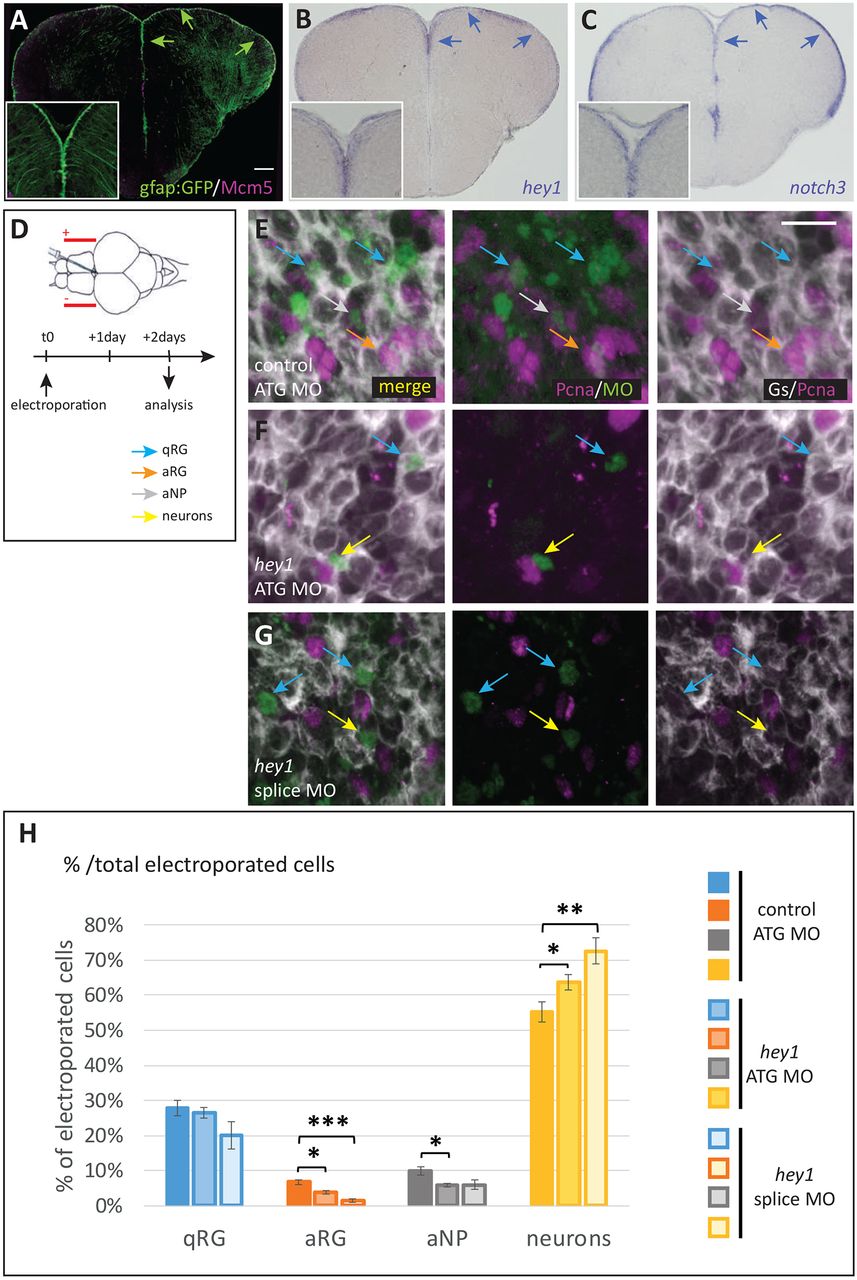
Hey1 activity maintains the proliferating progenitor state in the adult pallial germinal zone. (A) Cross-section of a gfap:gfp transgenic pallium at a mid-anteroposterior level, double immunostained for GFP (RGs) and Mcm5 (proliferating cells). Progenitor cells (qRGs, aRGs and aNPs) are confined to the ventricular zone (arrows, see high magnification inset). (B,C) Expression of hey1 and notch3 revealed by in situ hybridization on cross-sections of the adult pallium (same level as in A). Expression is confined to the VZ (arrows). (D) Experimental scheme to assess Hey1 function. hey1 (or control) fluorescein-labelled morpholinos (MO) are injected into the brain ventricle and electroporated. The fate of MO-inheriting cells (fluorescein-positive) is assessed 2 days post-electroporation. (E-G) Representative examples of triple immunostaining to reveal cell states in cross-sections of electroporated pallia [green, fluorescein; grey, glutamine synthase (RGs); magenta, Pcna (proliferating cells)]. Examples of cell types are indicated with colour-coded arrows, as defined in H. Scale bars: 50 μm in A-C; 10 μm in E-G. (H) Quantification of cell state/type changes following Hey1 blockade. The proportion of each cell state/type within the MO-inheriting population is plotted. The proportion of neurons is significantly increased upon Hey1 blockade, whereas the proportion of proliferating cell types (aRGs and aNPs) is significantly decreased. The proportion of qRGs is unchanged [hey1 ATG MO versus ATG control MO, P=0.59; hey1 splice MO versus ATG control MO, P=0.09 (after Holm's correction)]. Number of cells counted per brain: 196-796 for control MO, 137-413 for hey1 ATG MO and 49-493 for her1 splice MO. n=3-5 brains per condition. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.