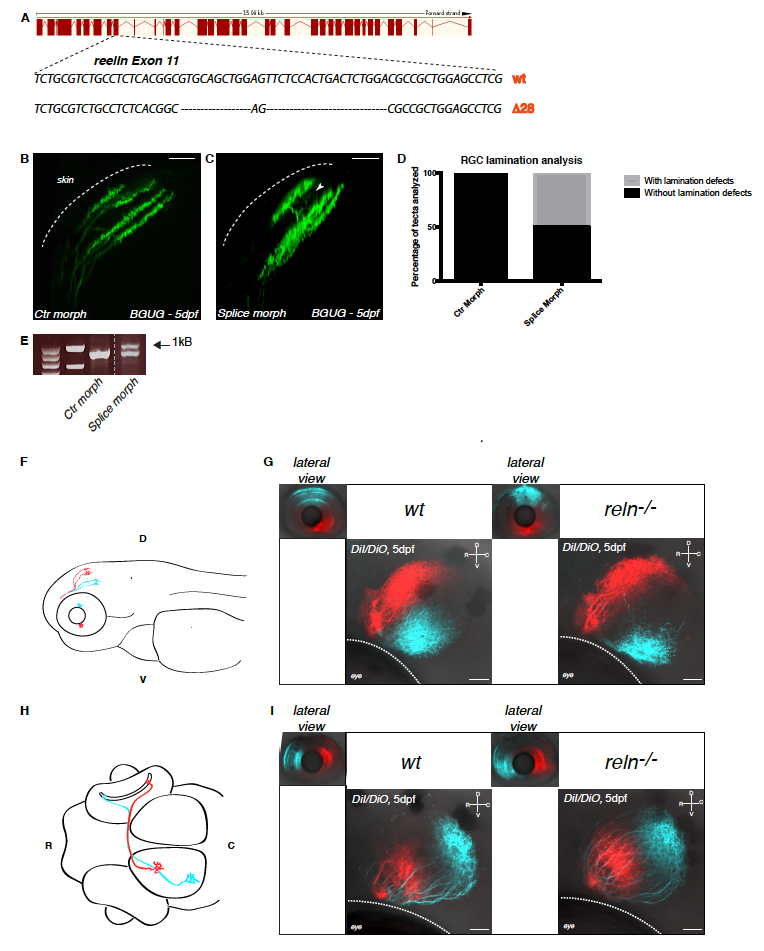
Fig. S1
Confirmation of the axonal lamination phenotype by antisense spliceblocking morpholino oligonucleotides against Reelin and analysis of retinotopic organization in Reelin mutant larvae. Related to Figure 1.
(A) Schematics of TALEN-mediated gene disruption at the reelin locus. The targeting of the gene induced a deletion of 28 base pairs (bp) in the reelin genomic locus leading to the generation of a premature STOP codon as described in Supplemental Table S1.
(B, C) Lateral projections of confocal stacks of the BGUG transgenic line, which is used to mosaic-label RGCs with GFP, that were injected with control (B) or reelin spliceblocking morpholino oligonucleotides (C). The white arrowhead in (C) indicates aberrant laminar targeting never observed in wild-type larvae. Scale bar = 20 μm.
(D) Quantification of the percentage of tecta with or without lamination defects in control (n=23/23) or splice-blocking morpholino (n=16/32) injected larvae.
(E) RT-PCR on cDNA extracted from 48dpf larvae injected with control morpholino or splice-blocking morpholino. The presence of an upper band in the splice-blocking morpholino-injected samples is the consequence of the retention in the transcript of the intron 12. The two first lanes indicate molecular markers.
(F) Lateral schematic view of a zebrafish larva highlighting dorso-ventral retinotopic targeting in the tectum. Axons from RGCs located in the dorsal retina terminate in the ventral tectal neuropil whereas axons from RGCs residing in the ventral retina project to the dorsal tectal neuropil. D = dorsal, V = ventral.
(G) Injections of lipophilic dyes DiI (red) and DiO (cyan) in dorsal and ventral quadrants of the contralateral retina show that retinotopic mapping to the optic tectum is not altered in reelin mutants (right panel) compared to wild-type embryos (left panel). D = dorsal, V = ventral, R = rostral, C = caudal. Scale bar = 30 μm.
(H) Dorsal schematic view of a zebrafish larva highlighting rostro-caudal retinotopic targeting in the tectum. Axons from RGCs located in the rostral retina terminate in the caudal tectal neuropil whereas axons from RGCs residing in the caudal retina project to the rostral tectal neuropil. R = rostral, C = caudal.
(I) Injections of lipophilic dyes DiI (red) and DiO (cyan) in rostral and caudal quadrants of the contralateral retina show that retinotopic mapping to the optic tectum is not altered in reelin mutants (right panel) compared to wild-type embryos (left panel). D = dorsal, V = ventral, R = rostral, C = caudal. Scale bar = 30 μm.