Fig. 5
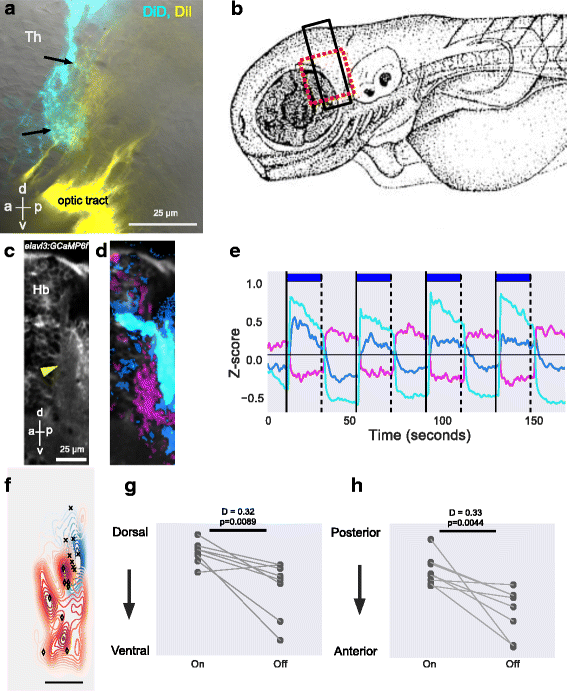
Anatomical and physiological characterization of the anterior thalamic neuropil. a. Lateral view of a 6-day-old fish following injection of DiD (cyan) into the dorsal neuropil of the left habenula and DiI (yellow) into the right retina. Arrows indicate terminals from retinal ganglion cells in the vicinity of fibers from habenula afferents. See Additional file 5: Movie 5. b Illustration of a fish larvae, showing the region imaged in panel a (red box) and in panels c and d (black box). c–h Response in the anterior thalamic neuropil to pulses of light. c Average projection of a lateral view of an elavl3:GCaMP6f fish, showing the thalamic neuropil (arrowhead). d, e The response to four pulses of blue light. Colors show the K-means cluster centers represented in panel e. The regions responding to light ON and OFF are distinct in the thalamic neuropil. Responses can also be seen in the habenula. f–h Quantitation of the anterior thalamus neuropil response to light pulses in eight fish. f Contours show a bivariate kernel density estimate of neuropil pixel location for responses to ON (shades of blue) and OFF (shades of red) of blue light in eight fish. The two variables here are x and y of neuropil pixels. The orientation is same as panel d. Crosses indicate median location of response to light ON, while diamonds indicate median location of response to light OFF in each fish. The dorso-ventral and anterior-posterior positions of the median centers are shown in panels g and h, respectively. Each circle is one fish and lines join data points from the same fish. These panels show that ON and OFF responses have a different location, with OFF responses in a more anterior-ventral location. P values and test statistic (D) were obtained using Kolmogorov–Smirnov test on cumulative distribution of pixel location to light ON and OFF from all fish. a anterior, p posterior, d dorsal, v ventral, Hb habenula, Th thalamus