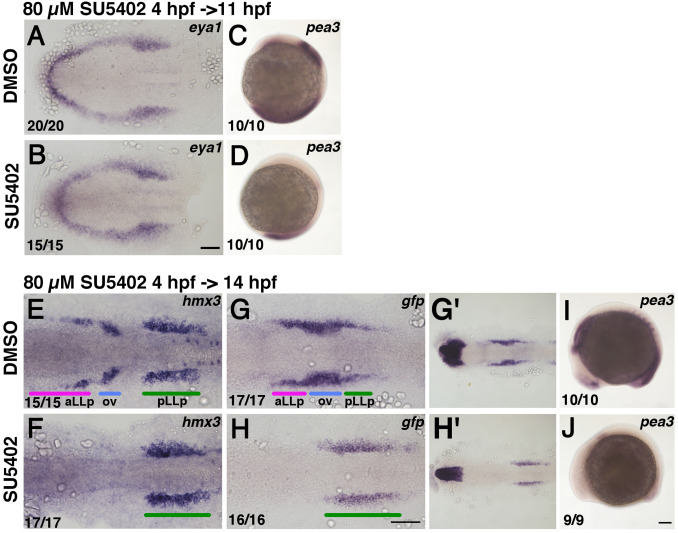
Fig. 3
Inhibition of Fgf activity suppresses aLLp formation but expands the pLLp. Duration of the inhibitor treatment and timing for fixation are indicated on the top-left of a group of pictures. After drug treatment embryos were immediately fixed and subjected to in situ hybridization. The drugs used (0.8% DMSO or 80 µM SU5402) are shown on the left. Numbers in the bottom-left indicate numbers of embryos showing the phenotype. (A, B) Flat-mounted embryos at 11 hpf stained with eya1. Anterior to the left. (E-H, G’, H’) Flat-mounted embryos at 14 hpf stained with hmx3 (E, F) and gfp (G, H, G’, H’). G’ and H’ are lower magnification views of G and H, respectively. Anterior to the left. (C, D, I, J) Lateral views of 11 hpf (C, D) and 14 hpf (I, J) embryos stained with pea3. Anterior is oriented to the top for C, D, whilst anterior to the left for I, J. Colored bars indicate the positions of the aLLp, otic vesicle and pLLp. Abbreviations: aLLp: anterior lateral line placode, ov: otic vesicle, pLLp: posterior lateral line placode. Scale bars: 100 µm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 431(2), Nikaido, M., Acedo, J.N., Hatta, K., Piotrowski, T., Retinoic acid is required and Fgf, Wnt, and Bmp signaling inhibit posterior lateral line placode induction in zebrafish, 215-225, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.