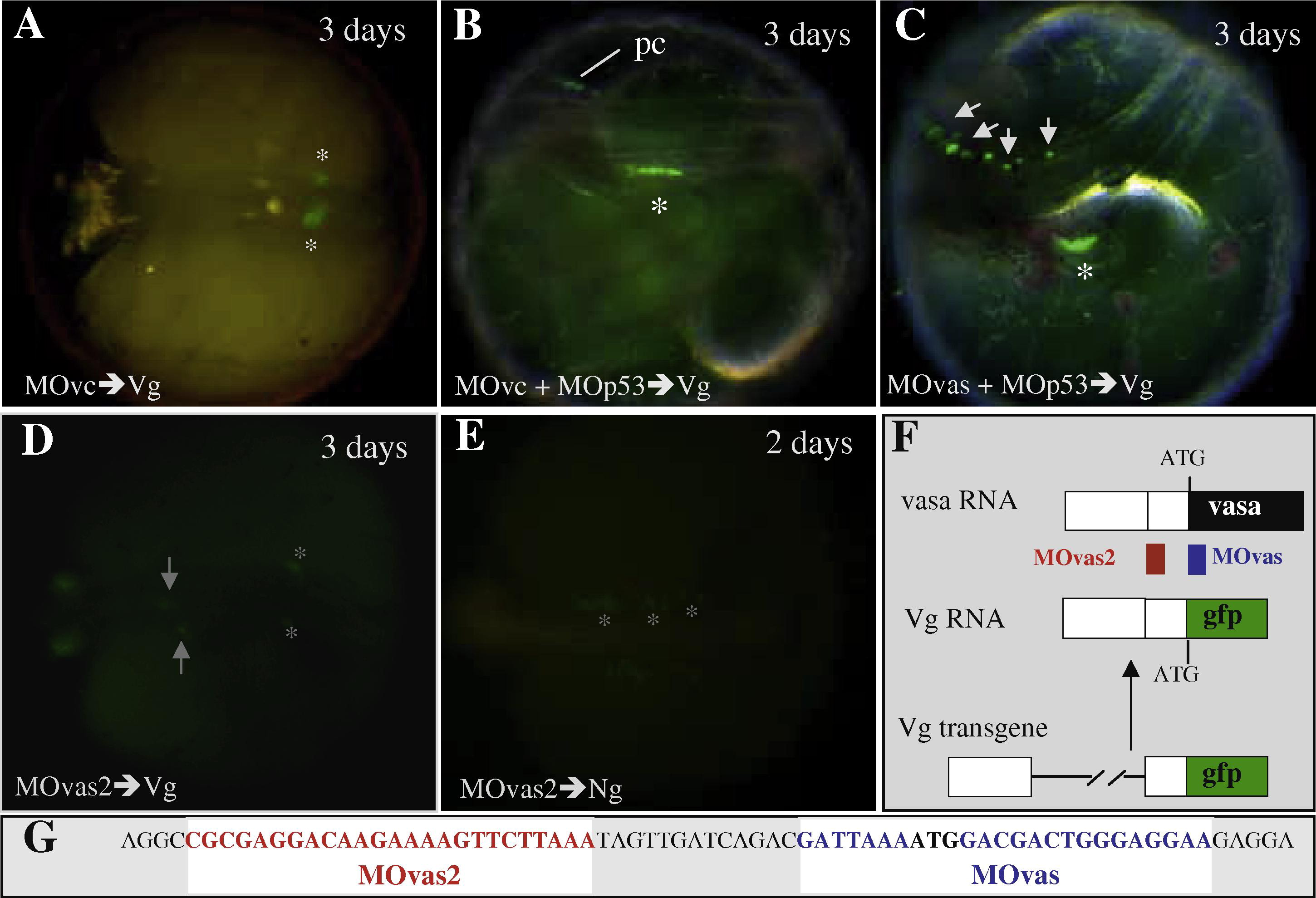
Fig. 3
Specificity of vasa morpholinos. (A–C), Coinjection of MOp53 does not prevent the PGC migration defect caused by vasa morpholino. Morpholinos were zygotically injected at 1.5 ng and PGC distribution was analyzed from 2 dpf onwards. (A) Injection of MOvc alone. (B) injection of MOvas together with MOp53 against the medaka p53 mRNA. (C) Coinjection of MOvas and MOp53. MOp53 does not prevent MOvas-induced ectopic PGCs. (D–G) MOvas2 prevent its translation. (D) MOvas2 reduces the GFP signal of PGCs in Vg embryos. (E) MOvas2 does not reduce the GFP intensity in Ng embryo. (F and G) Positions and the target sequences of MOvas and MOvas2 on the vasa cDNA. ATG, initiation codon; open box, untranslated region; filled box, coding sequence. MOvas acts on the endogenous vasa RNA only, whereas MOvas2 can target both the vasa RNA and transgene-derived Vg RNA, thus reduces the GFP signal in PGCs. Asterisks depict normally distributed PGCs, arrows indicate ectopic PGCs.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 126(5-6), Li, M., Hong, N., Xu, H., Yi, M., Li, C., Gui, J., Hong, Y., Medaka vasa is required for migration but not survival of primordial germ cells, 366–381, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.