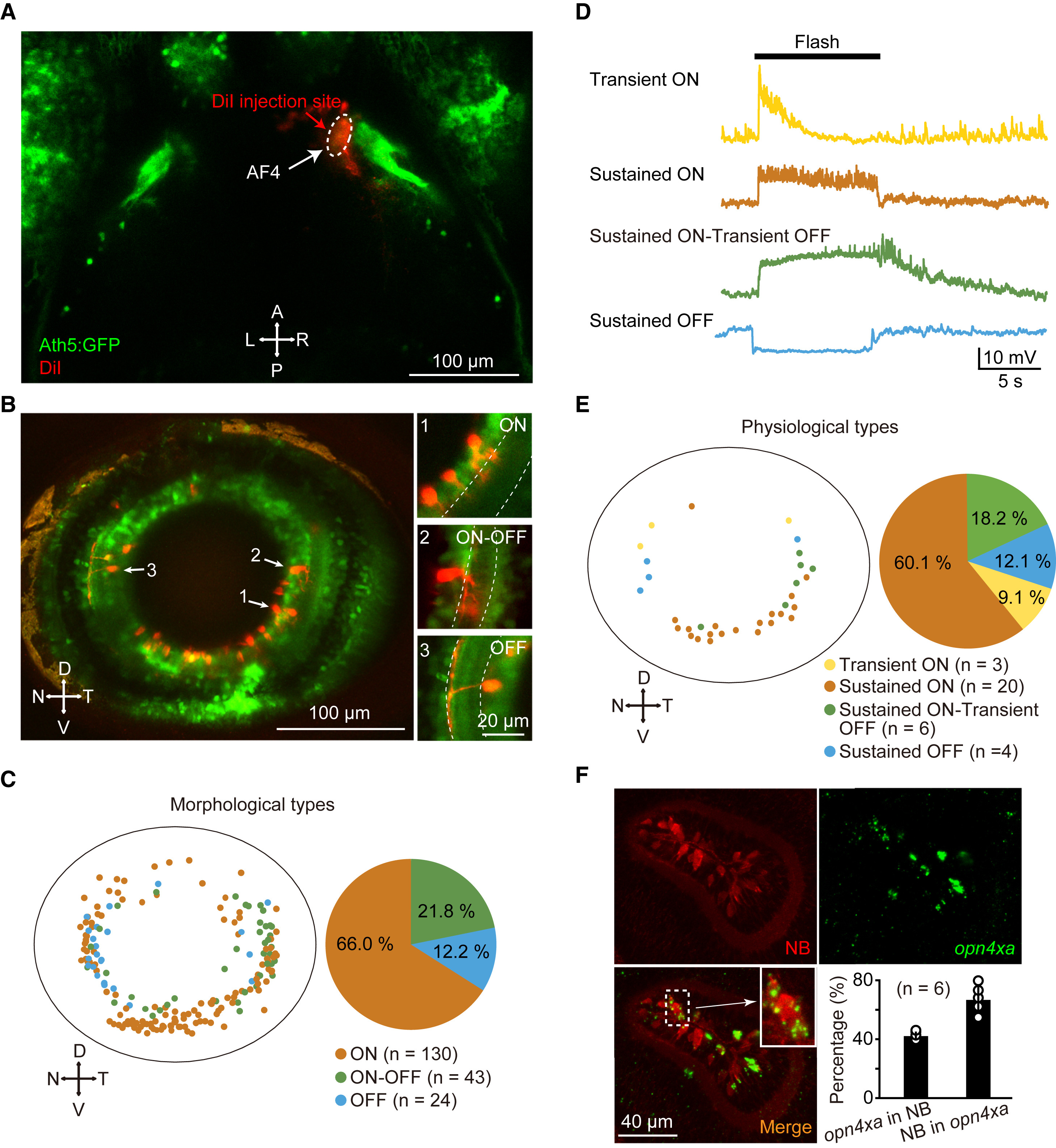
Fig. 6
Properties of AF4-Projecting RGCs
(A) Projected confocal image showing local injection of DiI into the AF4 in a 5-dpf Tg(Ath5:GFP) larva.
(B) Left: projected confocal image showing retrograde labeling of AF4-projecting RGCs in contralateral retina. Right: sample images showing three morphological types of RGCs: ON, OFF, and ON-OFF, dendrites of which stratify in the inner part of the interplexiform layer (IPL), the outer part of the IPL, and both the inner and outer parts of the IPL, respectively. Dashed lines represent the IPL boundary. To clarify the morphology of the three sample cells, different ranges of images along z axis were projected. D, dorsal; N, nasal; T, temporal; V, ventral.
(C) Spatial distribution and percentage of the three morphological types of AF4-projecting RGCs. Data were obtained from 15 larvae examined.
(D) In vivo whole-cell recording of retrogradely labeled RGCs showing four physiological types of AF4-projecting RGCs: transient ON, sustained ON, sustained ON-transient OFF, and sustained OFF. 10 s flashes were applied. All traces were averaged from four trials.
(E) Spatial distribution and percentage of the four physiological types of AF4-projecting RGCs. Data were obtained from nine larvae.
(F) Staining of neurobiotin (NB) (top, left) and fluorescence in situ hybridization of opn4xa (top, right). Inset: an enlarged image showing a NB- and opn4xa-positive RGC. Bottom right: percentages of AF4-projecting RGCs with opn4xa-positive signals (left bar) and opn4xa signals co-localized with AF4-projecting RGCs (right bar). Data were obtained from six larvae.
The numbers in the parentheses represent the numbers of RGCs examined (C and E).
See also Figure S6.