Fig. 2
Motor Neurons Other Than CaPs Receive Limited CSF-cN Input
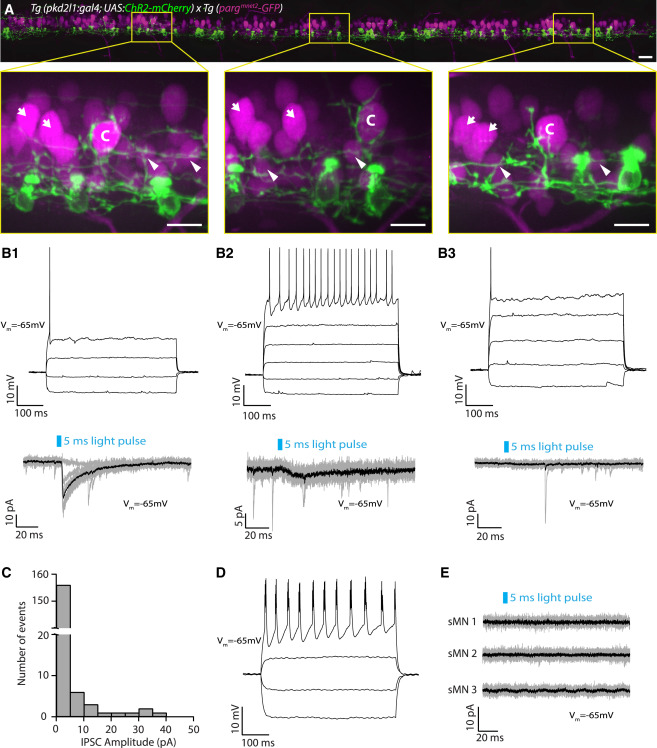
(A) Motor neurons and CSF-cNs labeled in the Tg(pargmnet2-GFP; pkd2l1:gal4; UAS:ChR2-mCherry) transgenic line throughout the rostro-caudal axis (12 axial segments) at 3 dpf. Boxes with magnified images highlight extensive innervation of large dorsal CaP motor neurons (labeled “C”). However, other (non-CaP) primary motor neurons (indicated by arrows) and secondary motor neurons (indicated by arrowheads) do not exhibit the same extensive perisomatic innervation. Scale bars, 20 μm (top) and 10 μm (magnified boxes, bottom).
(B1–B3) Examples of whole-cell recordings from non-CaP primary motor neurons showing three types of postsynaptic responses observed.
(B1) Top: current-clamp recording of a primary motor neuron showing a single action potential in response to current injection (steps of 40 pA from −50 pA to +70 pA). Bottom: voltage-clamp recording from the same primary motor neuron (Vm = −65 mV) showing evoked IPSCs following 5-ms light pulses (black trace is the average of ten trials shown in gray).
(B2) Top: current-clamp recording of a primary motor neuron showing tonic action potentials in response to current injection (steps of 40 pA from −50 pA to +150 pA). Bottom: voltage-clamp recording from the same primary motor neuron (Vm = −65 mV) showing small evoked IPSCs following 5-ms light pulses (black trace is the average of ten trials shown in gray).
(B3) Top: current-clamp recording of a primary motor neuron showing a single action potential in response to current injection (steps of 40 pA from −30 pA to +130 pA). Bottom: voltage-clamp recording from the same primary motor neuron (Vm = −65 mV) showing no IPSCs following 5-ms light pulses (black trace is the average of ten trials shown in gray).
(C) Histogram of IPSC current amplitudes from non-CaP primary motor neurons (mean 1.78 ± 0.42 pA; n = 17 cells, 170 trials).
(D) Current-clamp recording of a secondary motor neuron showing bursts of action potentials in response to current injection (steps of 20 pA from −30 pA to +30 pA).
(E) Example of voltage-clamp recordings from secondary motor neurons (sMNs) (Vm = −65 mV) showing no IPSCs following 5-ms light pulses (black trace is the average of ten trials shown in gray). IPSCs in secondary motor neurons were never observed following CSF-cN stimulation (n = 10).
See also Table S1.