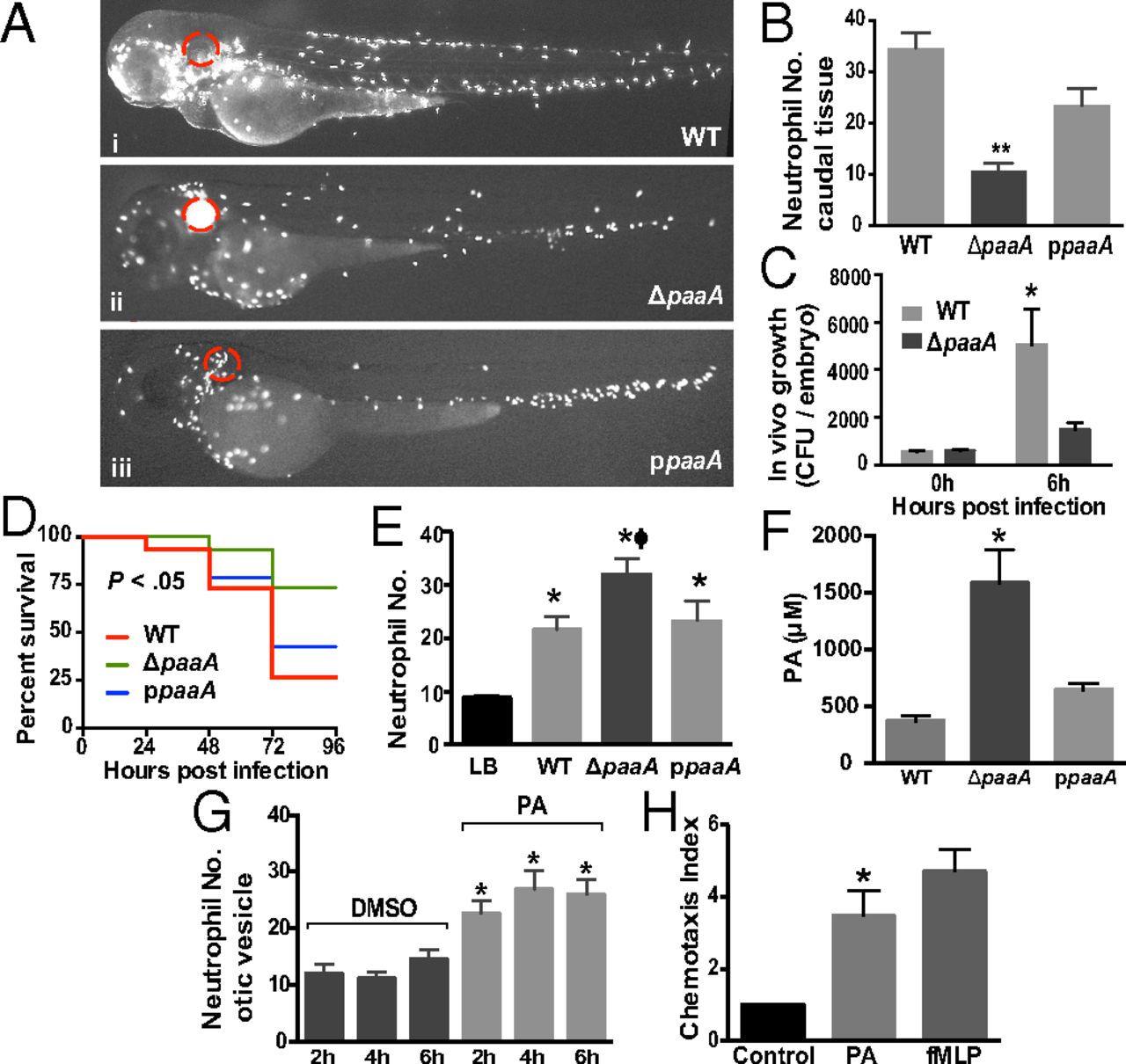
Fig. 5
PA is a bacterial-driven chemoattractant. (A) Neutrophil accumulation imaged 48 hpi of the otic vesicle (red circle). (B) The observed neutrophil clustering was associated with a reduction in neutrophils normally resident in the caudal hematopoietic tissue assessed at 48 h. The functional effect of this neutrophilic response to A. baumannii ΔpaaA infection was a reduced bacterial burden (C) and increased zebrafish survival (D) compared with wild-type A. baumannii and the complemented strain (ppaaA; P value is a comparison of ΔpaaA and ppaaA by log-rank test). (E) Attraction of neutrophils to the otic vesicle 6 hpi of culture filtrate. (F) Concentration of PA in culture filtrates. (G) Injection of purified PA into the otic vesicle was sufficient to attract a greater number of neutrophils within 2 h of injection compared with PBS solution. (H) Neutrophil chemotaxis toward PA (0.05 M) in an ex vivo neutrophil transwell migration assay using mouse-derived neutrophils. fMLP was used as a positive control. For all experiments, column bars represent the mean ± SEM, performed at least in triplicate, and the asterisks denote comparison between wild-type A. baumannii and ΔpaaA for B, C, and F, between LB and wild-type, ΔpaaA, and ppaaA for E, and between PA and PBS control for G and H; letter Φ denotes comparison between wild-type and ΔpaaA for E by one-way ANOVA (Kruskal–Wallis test, *P ≤ 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ΦP ≤ 0.05). (Magnification: 10×.)