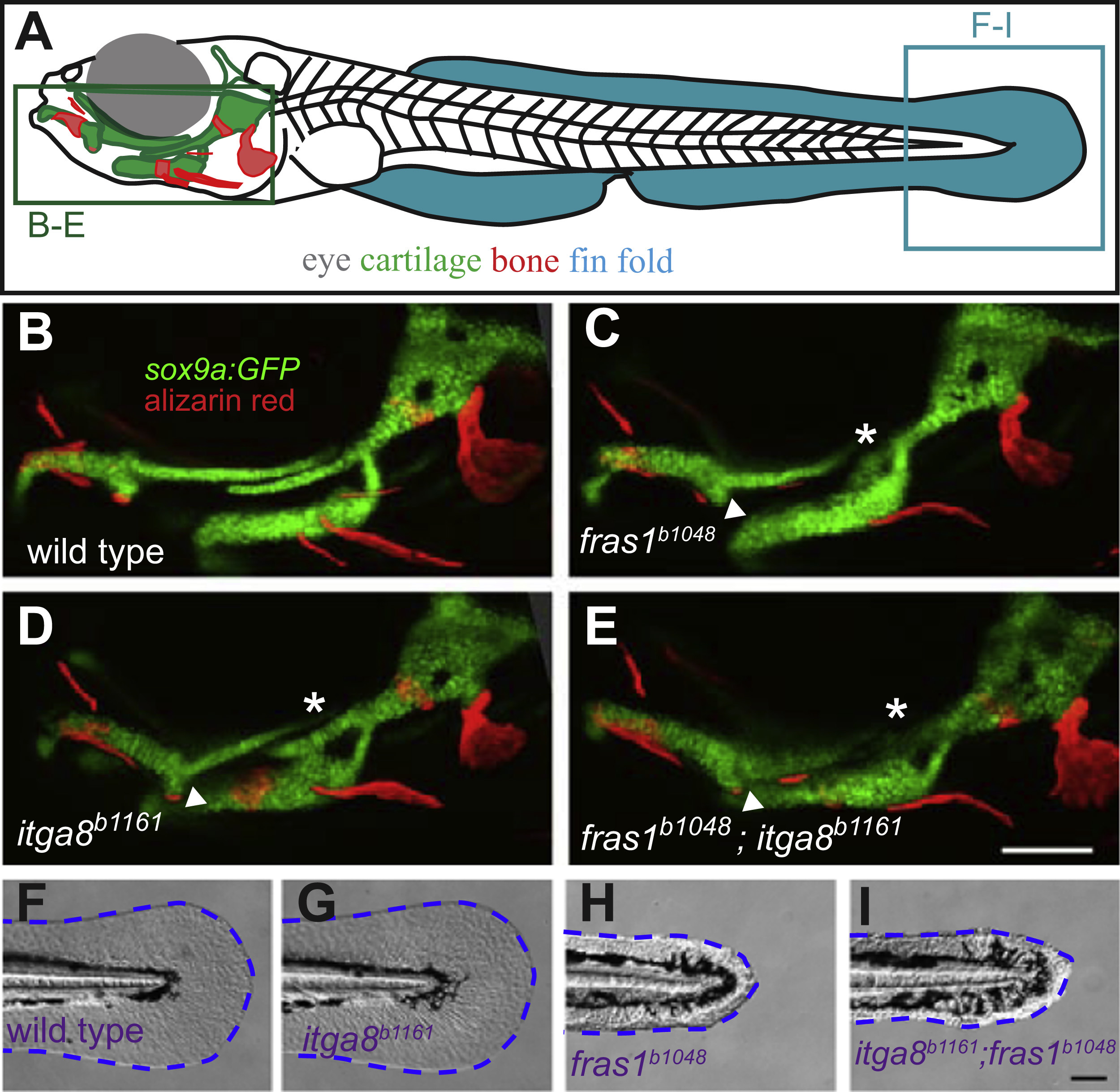
Fig. 2
Comparison of skeletal, endodermal, and tail ectoderm phenotypes between wild type, itga8b1161 mutants, fras1b1048 mutants, and itga8b1161;fras1b1048 double mutants. (A) Illustration of a zebrafish larva, indicating regions shown in subsequent (B-I) panels. (B-E) Skeletal morphology is revealed using sox9a:EGFP expression (cartilage) and alizarin red staining (bone) at 7 dpf; itga8 and fras1 single and double mutants display similar cartilage defects, in particular, Meckel’s-palatoquadrate joint fusion (arrowhead) and symplectic-ceratohyal fusions (asterisk). (F-I) Bright field images showing normal fin fold morphology (outlined blue) in (F) wild type and (G) itga8b1161 individuals versus the “blister phenotypes” in (H) fras1b1048 and (I) itga8b1161;fras1b1048 mutants. Scale bars (E and I) are 100 µm. Scale bar in E applies to B-E; Scale bar in I applies to F-I.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 416(1), Talbot, J.C., Nichols, J.T., Yan, Y.L., Leonard, I.F., BreMiller, R.A., Amacher, S.L., Postlethwait, J.H., Kimmel, C.B., Pharyngeal morphogenesis requires fras1-itga8- dependent epithelial-mesenchymal interaction, 136-48, Copyright (2016) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.