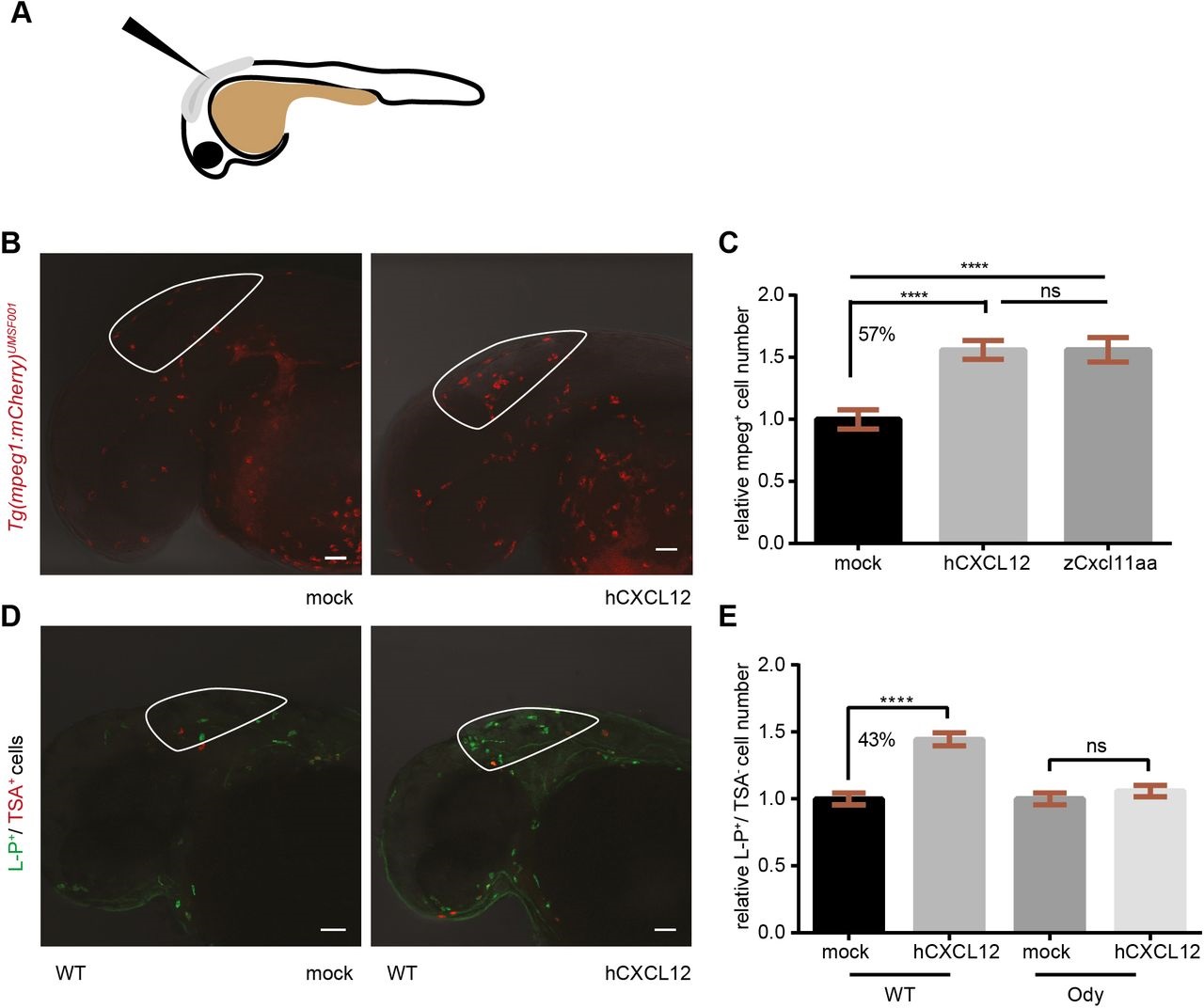
Fig. 4
Human CXCL12 triggers zebrafish macrophage migration in a Cxcr4-dependent manner. (A) Scheme of a 30- to 32-hpf embryo and injection site are shown. (B,C) Zebrafish macrophages were found to be responsive to human CXCL12 (0.4mg/ml) 3h after injection into the hindbrain ventricle (HBV) of 30- to 32-hpf embryos. No increase in macrophage number occurred when a mock solution (water) was inoculated. Zebrafish Cxcl11aa (1.5mg/ml) was used as a positive control (C). Data in C are pooled observations from two independent experiments (n=55 in mock; n=48 in hCXCL12; n=57 in zCxcl11aa). (D,E) Macrophages were recruited by human CXCL12 in a Cxcr4-dependent manner: a higher number (43%) of L-P+/TSA- cells was found in the HBV compared to the mock-injected group in wild-type (wt) siblings (D,E), whereas no differences were detected in the cxcr4b-/- (ody) mutants (E). In B, mCherry-expressing macrophages are recruited by hCXCL12 as in D, where L-P staining combined to TSA detection is used to distinguish macrophages (L-P+/TSA-) from neutrophils (L-P+/TSA+). ****P<0.0001, ns P>0.05 one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post-hoc test. Data in E are pooled observations from five independent experiments (n=171 in mock/wt; n=180 in hCXCL12/wt; n=139 in mock/ody; n=160 in hCXCL12/ody).