Fig. 4
Retinotectal Processing of Looming Stimuli
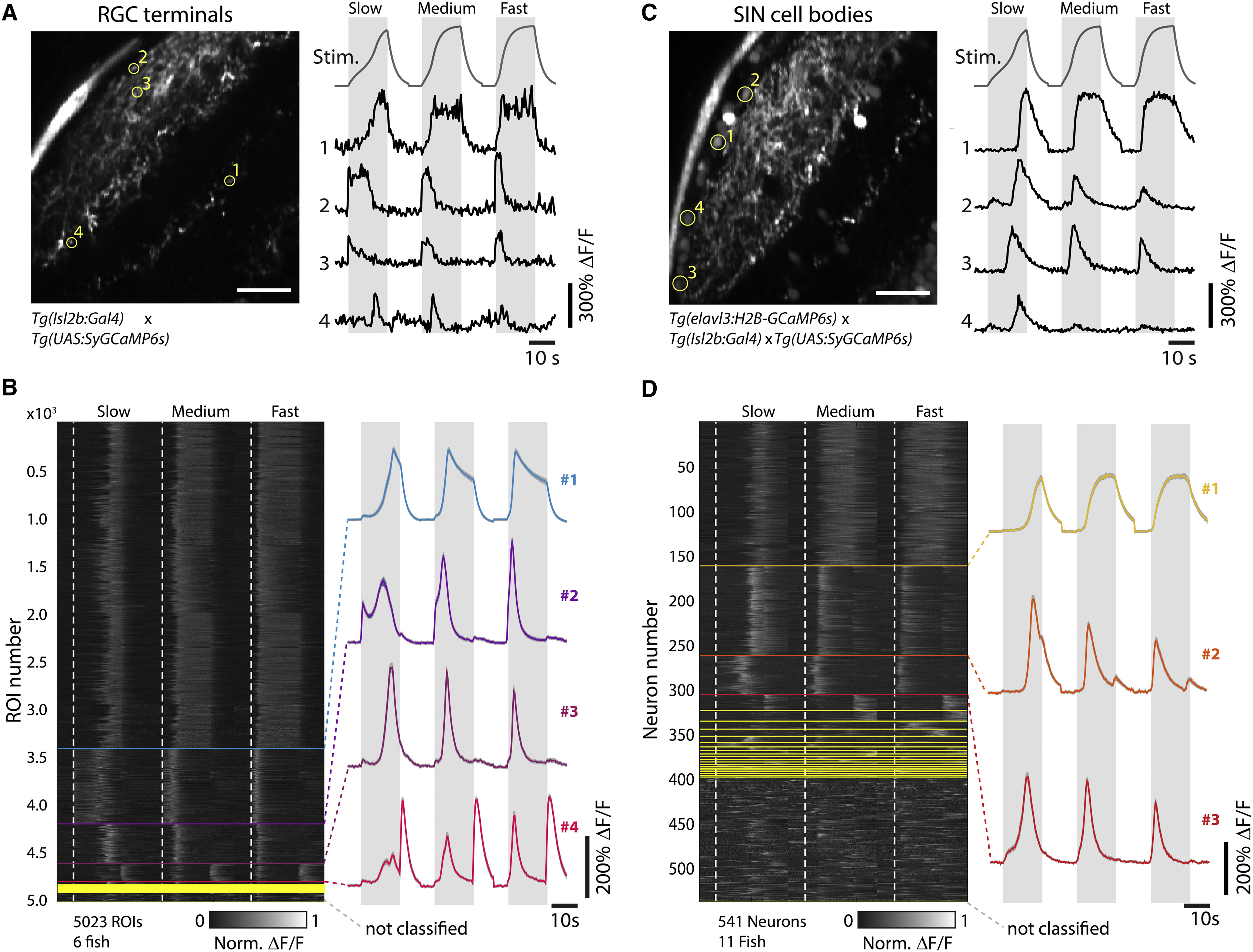
(A) Left panel is a representative imaging plane from a 5-dpf Tg(Isl2b:Gal4;UAS:SyGCaMP6s) fish, which specifically expresses GCaMP6s in the axon terminals of RGCs. Scale bar, 20 µm. Right panel shows traces from the four ROIs indicated on the left (yellow circles), with convolved looming stimulus time courses for slow (R/V = 2,730 ms), medium (R/V = 1,090 ms), and fast (R/V = 545 ms) stimuli shown on top for reference. Gray intervals denote stimulus duration.
(B) Left panel is a raster plot after regression cluster analysis of normalized ΔF/F responses for n = 5,023 RGC terminal ROIs across N = 6 fish, sorted according to the number of individual traces assigned to each respective cluster. Start frames for each stimulus are denoted by the dotted white, vertical lines. Different clusters are separated by horizontal lines. The right panel shows mean traces of the four main clusters (containing at least 2% of the total ROIs from at least five fish, top to bottom: clusters 1–4, N = 3,420, 788, 413, and 192 ROIs, respectively).
(C) The left panel shows a representative imaging plane from a 5-dpf Tg(elavl3:H2B-GCaMP6s;Isl2b:Gal4;UAS-SyGCaMP6s) fish, which labels SINs. Scale bar, 20 µm. The right panel shows traces from the four ROIs indicated on the left (yellow circles).
(D) Left panel is a raster plot after regression cluster analysis of normalized ΔF/F responses for n = 541 SIN neurons across N = 11 fish, sorted according to the number of individual traces assigned to each respective cluster. Right panel shows mean traces of the three main clusters (containing at least 2% of the total neurons from at least eight fish, top to bottom: clusters 1-3, N = 163, 101, and 44 neurons, respectively).