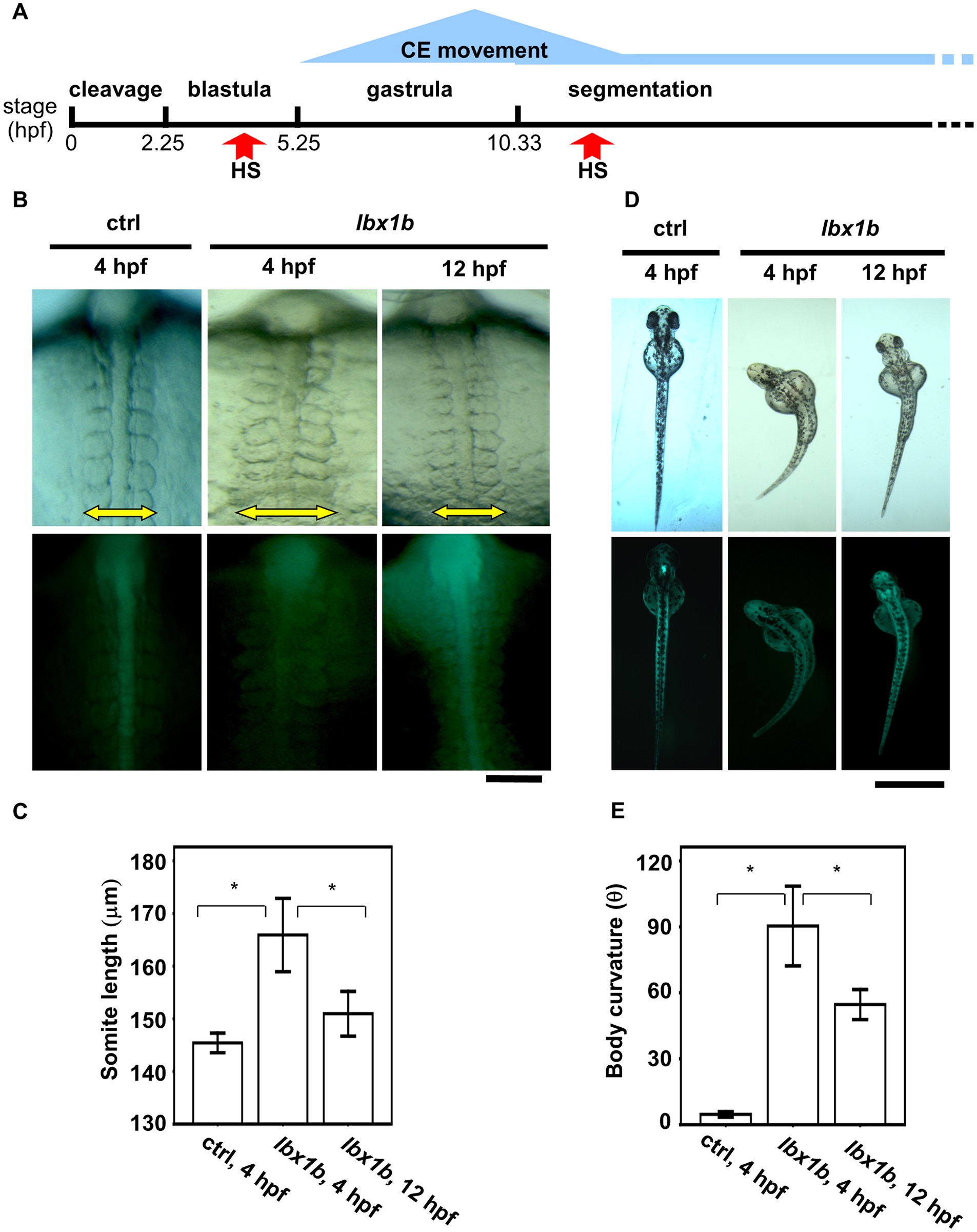
Fig. 4
Time-dependent induction of somite mediolateral elongation and body curvature by lbx1b overexpression.
(A) A schematic diagram of zebrafish early developmental stages. Convergent extension (CE) is mainly involved in gastrulation. (B) Comparison of somite mediolateral length (16 hpf) between Tg(hsp:Gal-VP; UAS:EGFP) with heat shock (HS) treatment at 4 hpf (ctrl 4 hpf), Tg(hsp:Gal-VP; EGFP:UAS:lbx1b) with HS at 4 hpf (lbx1b 4 hpf), and Tg(hsp:Gal4-VP; EGFP:UAS:lbx1b) with HS at 12 hpf (lbx1b 12 hpf). A significant elongation of somite mediolateral length (yellow arrow in the upper panels) was observed in the lbx1b embryos at 4 hpf. The scale bar represents 100 µm. (C) Quantitative analysis of somite mediolateral length in embryos at 16 hpf. A significant difference was observed between ctrl at 4 hpf (n = 16) and lbx1b at 4 hpf (n = 13), and lbx1b at 4 hpf (n = 13) and lbx1b at 12 hpf (n = 14), *p < 0.01. (D) Comparison of body curvature (48 hpf) between Tg(hsp:Gal-VP; UAS:EGFP) with HS treatment at 4 hpf (ctrl 4 hpf), Tg(hsp:Gal-VP:EGFP:UAS:lbx1b) with HS at 4 hpf (lbx1b 4 hpf), and Tg(hsp:Gal-VP:EGFP:UAS:lbx1b) with HS at 12 hpf (lbx1b 12 hpf). More severe curvature of the body axis was induced in lbx1b embryos at 4 hpf than in lbx1b embryos at 12 hpf. The scale bar represents 1 mm (E) Quantitative analysis of body curvature at 48 hpf. A significant difference was observed between ctrl 4 hpf (n = 13) and lbx1b 4 hpf (n = 10), and between lbx1b 4 hpf (n = 10) and lbx1b 12 hpf (n = 11), *p < 0.05. The severity of body curvature was quantified by the angle described in the legend of Fig 3. Both driver transgenic and responder transgenic fish were F2 lines.