Fig. 2
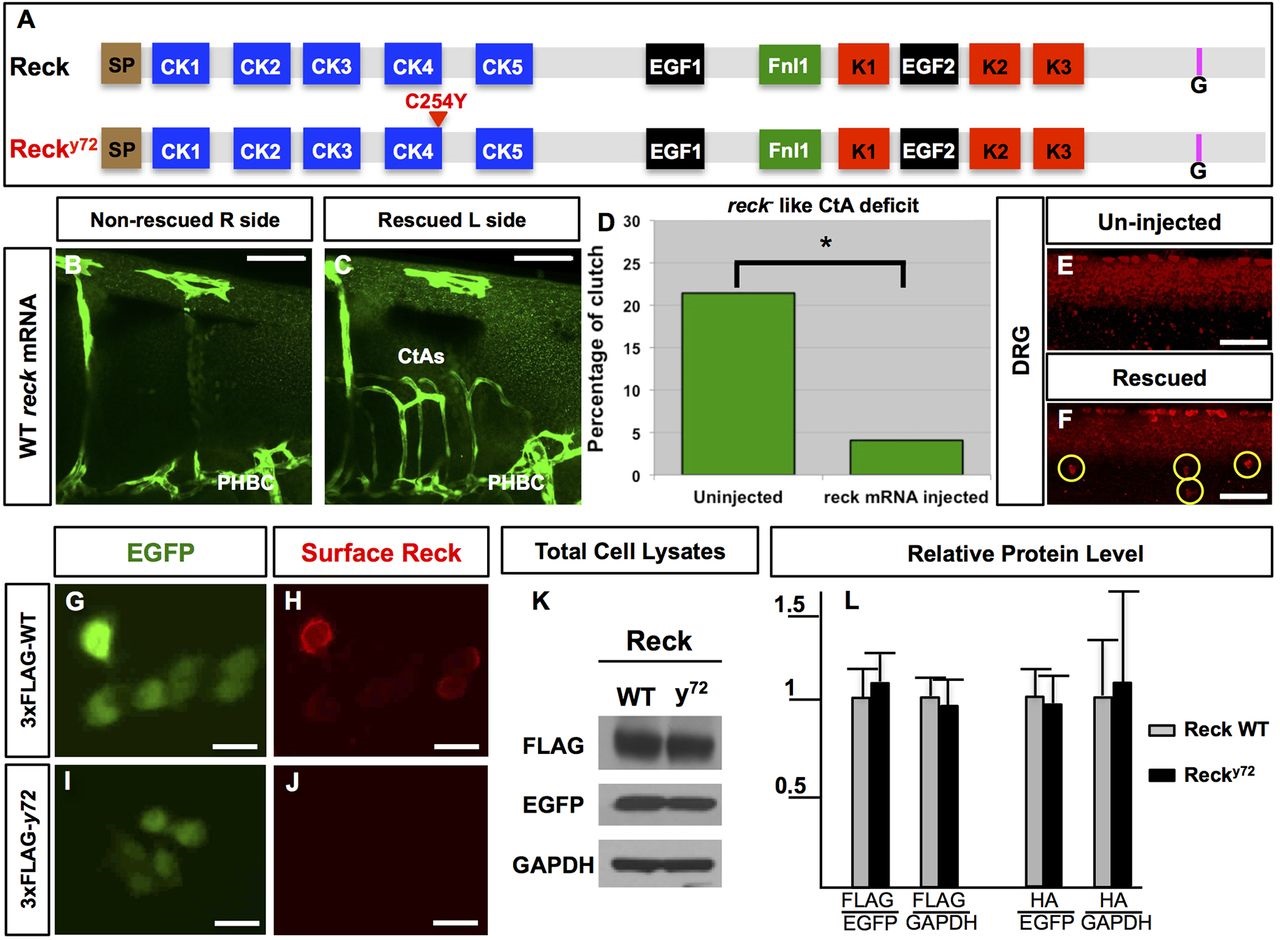
nft y72 is a genetically null allele of reck. (A) WT zebrafish Reck (top) is 955 aa long and features the same domains and motifs found in mammalian RECK (Takahashi et al., 1998). N-terminal signal peptide (SP; brown), cysteine knot motifs (CK1-5; blue), epidermal growth factor-like repeats (EGF1-2; black), fibronectin-like type I module (Fnl1; green), Kazal motifs (K1-3; red), C-terminal GPI transferase cleaveage site (G; pink). Mutant Recky72 (bottom) harbors a missense amino acid change in an evolutionarily conserved Cys residue within CK4. (B-F) Providing WT reck mRNA to reck y72 mutants restores formation of both CtAs (B-D) and DRG (E,F). Embryos with unilateral CtA rescue {B,C; endothelium, green [Tg(fli1a:eGFP)y1]} or bilateral DRG rescue (F; yellow circles, red HuC immunofluorescence; only one side shown). Quantification of CtA rescue expressed as the percentage of embryos (from incrossing heterozygous mutant carriers) with reck-like CtA deficits (D). (G-L) Exogenous co-expression of epitope-tagged zebrafish Reck (WT Reck or mutant Recky72) with cytosolic EGFP in cultured mammalian cells. (G-J) Immunofluorescence-based detection of surface 3×FLAG-Reck (red) and EGFP fluorescence (green) in non-permeabilized 293T cells. 3×FLAG-Recky72 fails to reach the cell surface (J). (K,L) WT and mutant Recky72 expressed in COS7 cells show similar abundance. (K) Western blot of total cell lysates from cells expressing WT or mutant 3xFLAG-Reck. (L) Densitometry-based quantification total cell lysates from cells expressing WT Reck or mutant Recky72 zebrafish proteins tagged with 3×FLAG or 2×HA. Protein levels normalized with EGFP and GAPDH. Error bars: s.e.m. Scale bars: 50µm in B-C, 100µm in E,F and 10µm in G-J. See also Figs S2, S3, Movies 1-14 and Table S1.