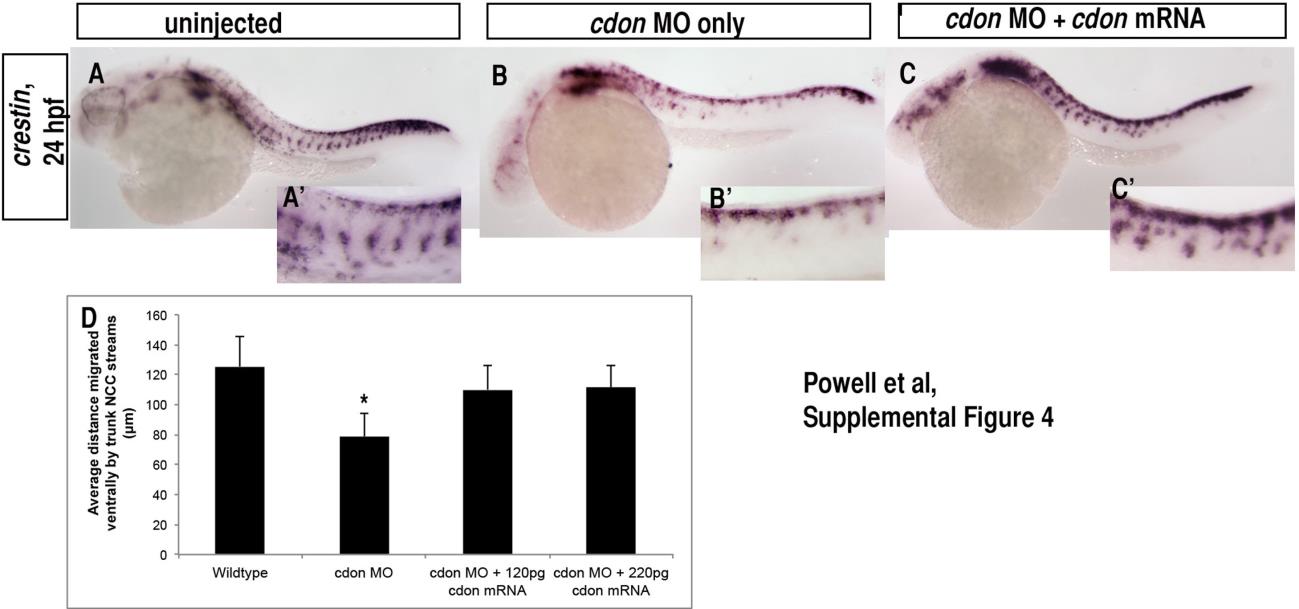
Fig. S4
cdonmRNA can rescue the cdon morphant phenotype. (A)–(C) Rescue of crestin expression at 24 hpf following cdon mRNA and MO co-injection. While injection of cdon ATG MO alone resulted in aberrant NCC migration (Fig. 2), co-injection with 120–220 pg of cdon mRNA resulted in the development of a greater number of embryos that had migratory streams and do not display the cdon morphant phenotype (n=12/119 or 10% compared to 84% morphant phenotype observed in MO injected alone.) (A′)–(C′) Higher magnification of NCC migratory streams in all conditions. The partial rescue of the cdon morphant phenotype by co-injection with cdon mRNA suggests that the cdon ATG MO specifically targets cdon. (D) Quantification of the average distance migrated by NCCs: wildtype=125.4 µm, cdon MO=78.8 µm, cdon MO+120 pg cdon mRNA=110 µm, cdon MO+220 pg cdon mRNA=111.5 µm;* p<0.0001 by ANOVA.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 407(2), Powell, D.R., Williams, J.S., Hernandez-Lagunas, L., Salcedo, E., O'Brien, J.H., Bruk Artinger, K., Cdon promotes neural crest migration by regulating N-cadherin localization, 289-99, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.