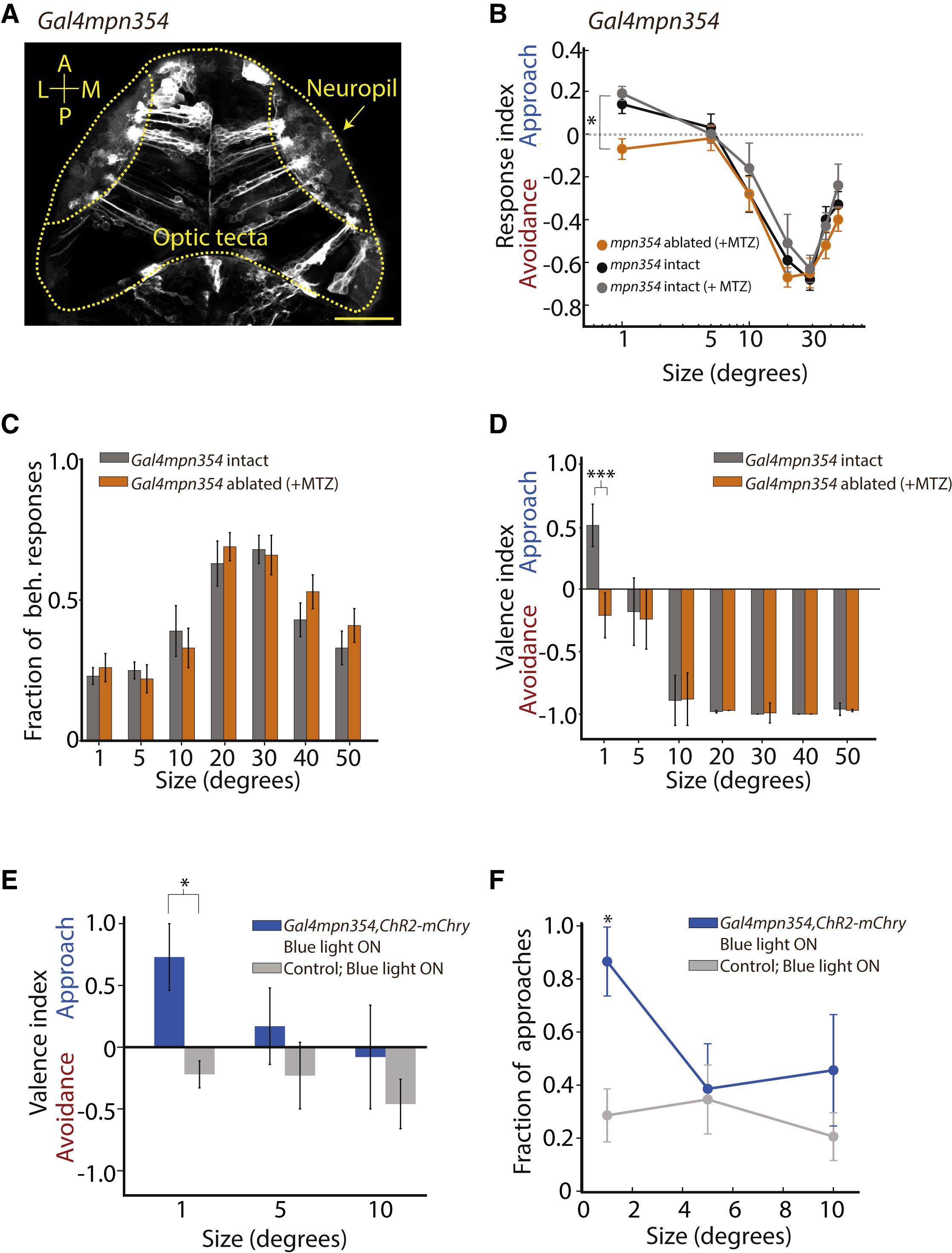
Fig. 3
Ablation and Activation of Gal4mpn354 Neurons Alter Behavioral Tuning in Opposite Directions
(A) Expression pattern in the 5-dpf optic tectum in a Gal4mpn354, UAS:Dendra fish.
(B) R.I. of Gal4mpn354, UAS:Nfsb-mChry larvae (MTZ-treated, n = 31, orange; no MTZ, n = 24, black) and Gal4mpn354, UAS:Dendra (MTZ-treated, n = 12, gray). Following ablation, the R.I. for a 1° dot switches from approach to avoidance (two-way ANOVA; Tukey’s correction; p at 1° = 0.038 and 0.032).
(C) The fraction of behavioral responses is not changed in Gal4mpn354-ablated larvae (p = 0.647, 0.621, and 0.655 at 1°, 5°, and 10° sizes, respectively).
(D) V.I. plots of fish used in (B). At 1°, V.I. is switched from approach to avoidance following ablation of Gal4mpn354 neurons (Fisher’s exact test; p at 1° = 0.0003; p = 1.00 at 5°; p = 1.00 at 10°).
(E and F) ChR2 activation of Gal4mpn354 neurons enhances approach behaviors at small sizes. (E) The V.I. for Gal4mpn354 neurons is shifted to approach when compared to wild-type siblings exposed to the same blue light stimulation (Fisher’s exact test; p = 0.015 at 1°). (F) The fraction of approaches is significantly increased at 1° when Gal4mpn354 neurons are activated (unpaired t test; Bonferroni correction; uncorrected p = 0.014 at 1°).
For all panels, error bars indicate the SEM. p < 0.05; p < 0.005; p < 0.0005. See also Figure S5 and Movie S3.