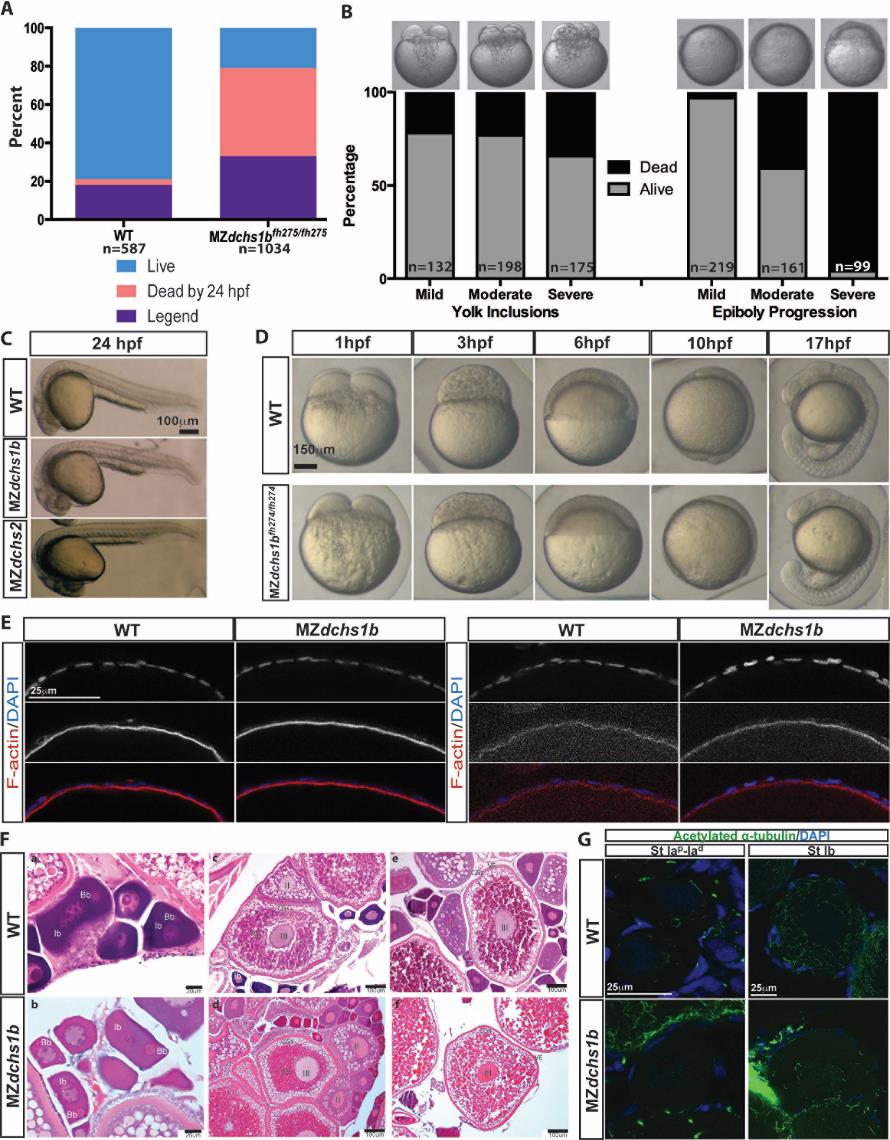
Fig. S2
Survival, morphology, and histology of WT and dchs mutants
A. Survival and fertility for WT (n=587) and MZdchs1bfh275/fh275 (n= 1034) mutant embryos.
B. Survival of MZdchs1bfh275/fh275 embryos based on severity of yolk inclusions and delayed epiboly phenotypes.
C. Morphology of WT, MZdchs1bfh275/fh275, and MZdchs1bstl1/stl1 embryos at 24 hpf.
D. Bright field images of WT and MZdchs1bfh27/fh274 time matched embryos at 1, 3, 6, 10, and 17 hpf.
E. Rhodamine phalloidin labels actin filaments in the cortical ooplasm and in the follicle cell layer. β-catenin localizes to the oocyte cortex or membrane in stage II oocytes of WT and dchs1b mutants.
F. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained ovary sections of WT and maternal dachsous mutant ovaries reveal a normal composition of oocytes. The primary oocytes of WT and Mdchs mutant ovaries are polarized as indicated by the presence of the Balbiani body (Bb) in stage Ib oocytes. Cortical granules begin to accumulate in stage II (II) oocytes of WT and Mdchs mutants and localize to the cortex in stage III (III) oocytes, which are distinguishable by the presence of yolk granules (Ygs). The structure of the vitelline envelope (VE) surrounding the oocyte is indistinguishable between WT and mutants. Images are representative of oocytes from 3 WT and 3 mutant females examined.
G. WT and dchs1b mutant oocytes stained with an antibody against acetylated α-tubulin.