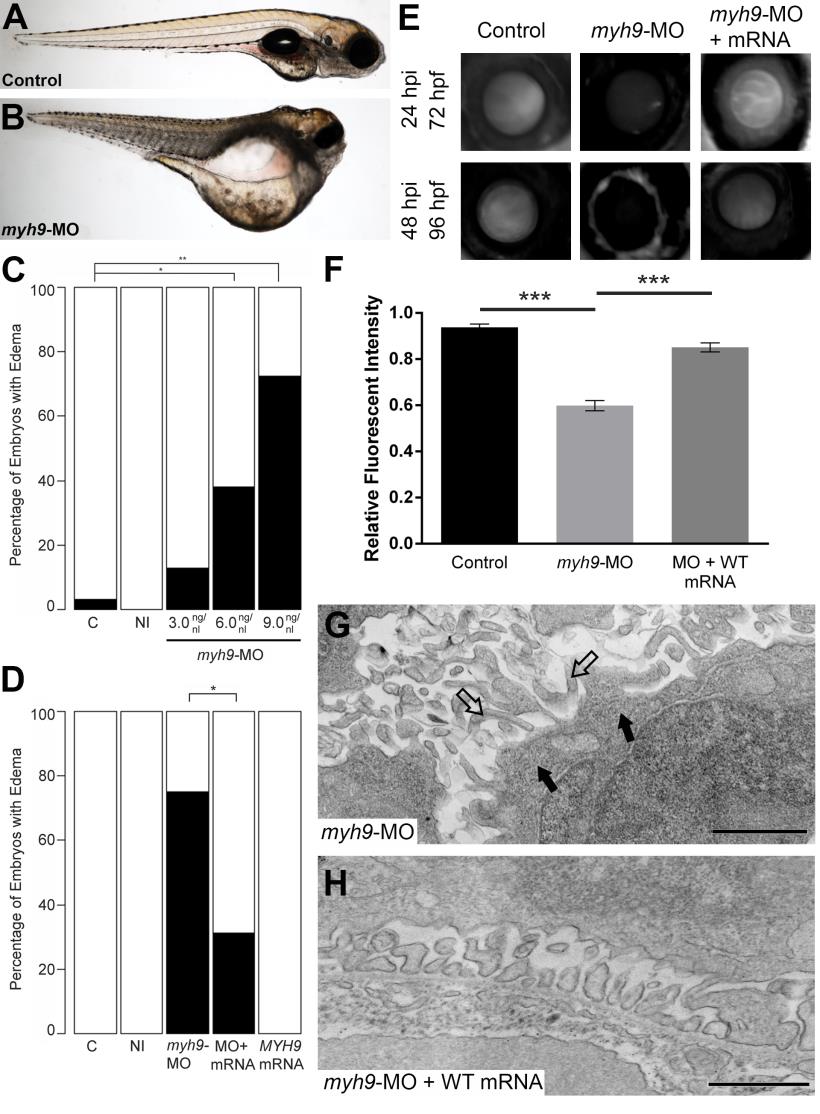
Fig. S3 myh9 suppression and complementation in developing zebrafish embryos.
We recapitulated data reported by Müller et al. for experimental comparison [17]. (A-B) Representative live images of sham-injected control and myh9 morpholino (MO) injected larvae at 5 dpf. (C) Injection of increasing doses of myh9 MO demonstrate dose-dependent effects when scored for generalized edema compared to control embryos at 5 dpf. (E-F) myh9 morphants also display filtration defects indicated by significantly increased dextran clearance. (D-F) Co-injection of wild-type human MYH9 mRNA (100pg/nl) significantly rescues edema formation and filtration defects observed in myh9 morphants. (G) As reported previously by Müller et al., myh9 morphants display ultrastructure abnormalities, including glomerular basement membrane thickening and the presence of microvillus protrusions in the urinary space. (H) These ultrastructural defects are rescued upon co-injection of wild-type human MYH9 mRNA (100pg). White bars, normal; black bars, edema; n = 49–70 and n = 13–29 embryos/injection batch for gross morphological scoring and glomerular filtration assays, respectively; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; filled arrowheads, glomerular basement membrane; open arrowheads, microvillus protrusions.