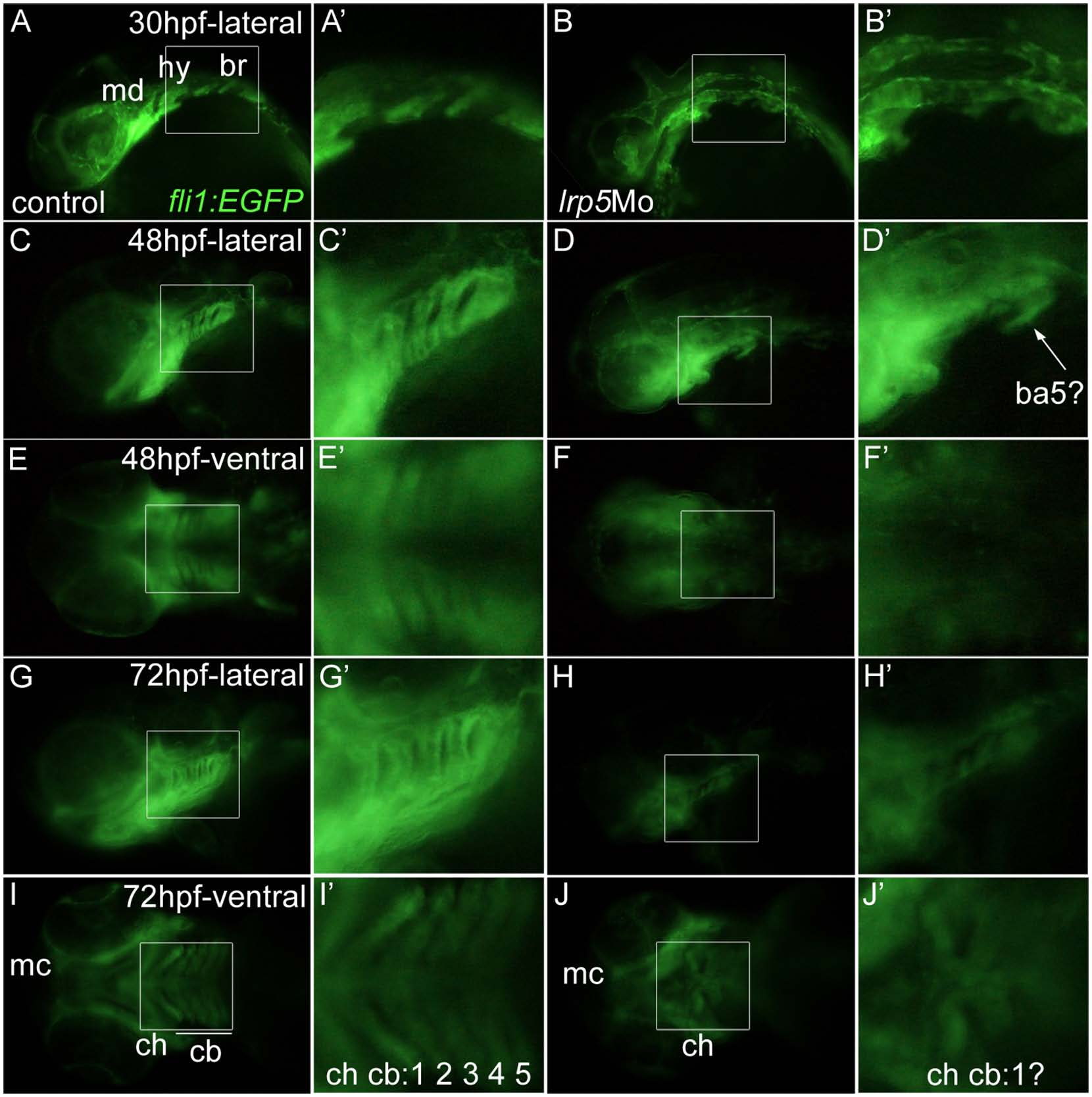
Fig. 7 Lower numbers of postmigratory CNCCs after lrp5 knock-down results in cranial skeleton malformations.
(A-B′) fli1:EGFP embryos at 30 hpf. (A,A′) Uninjected control embryo, (B,B′) lrp5 morphant. Note that mandibular (md), hyoid (hy) and three branchial (br) patches of postmigratory CNCCs are well defined in wild-type but defective in lrp5 morphants. (C-F′) fli1:EGFP embryos at 48 hpf. (C,C′) Uninjected control embryo in lateral view, (D,D′) lrp5 morphant lateral view, (E,E′) uninjected control embryo ventral view, (F,F′) lrp5 morphant ventral view. Note that metameric morphology of pharyngeal arches is absent in lrp5 morphant. Only one arch, most likely the 5th branchial arch is present (ba5?). (G-J′) fli1:EGFP embryos at 72 hpf. (G,G′) Uninjected control embryo in lateral view, (H,H′) lrp5 morphant lateral view, (I,I′) uninjected control embryo ventral view (J,J′) lrp5 morphant ventral view. Note that in wild-type, cranial elements like Meckel’s cartilage (mc), ceratohyal (ch) and 1st to 5th ceratobranchials (cb 1–5) can be distinguished, whereas in lrp5 morphant only mc and ch are detectable while cbs are undefined. Anterior is to the left in all images. Boxed areas in X are magnified in X′.