Fig. 3
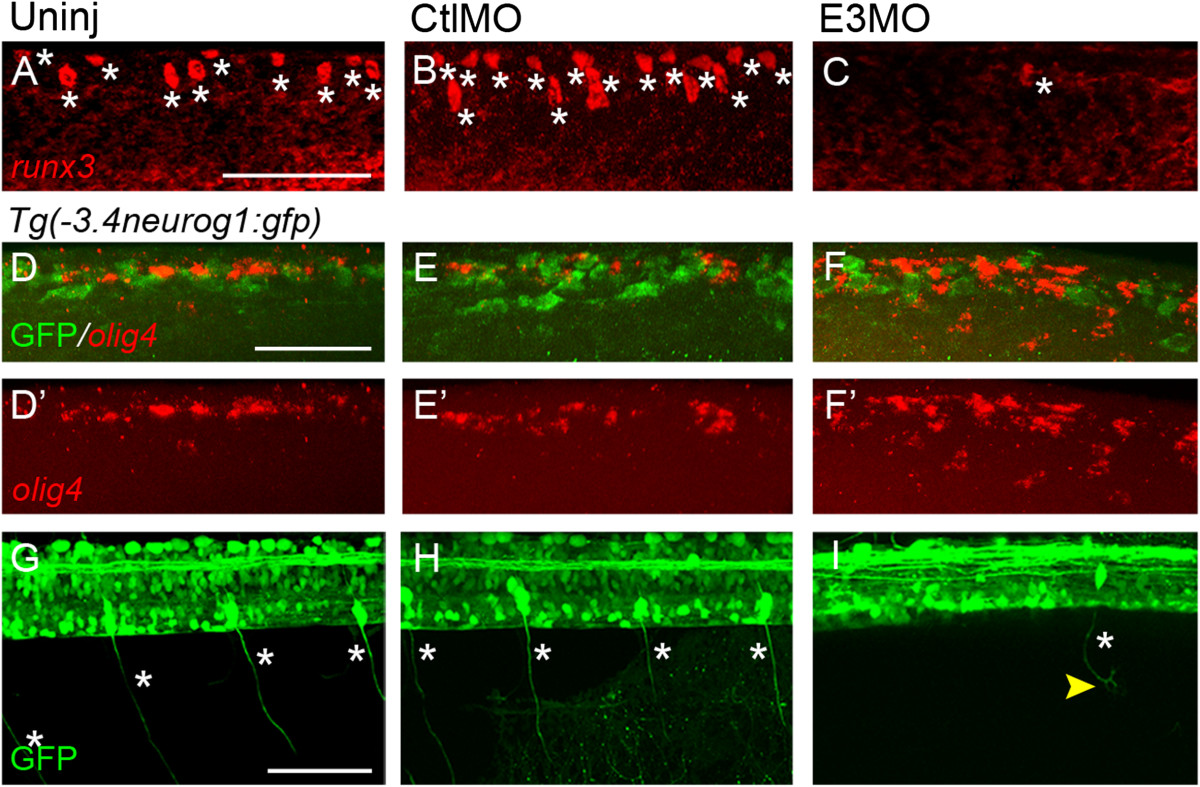
Islet1 knock-down affects sensory neuron differentiation. (A-C) In control embryos (A, B), Rohon-Beard cells (RBs) express runx3. Islet1 knock-down leads to fewer cells with robust expression of runx3 (C). The asterisk denotes a cell expressing the gene. (D-F′)Tg(-3.4neurog1:gfp)sb4 control (D-E′) and E3 morphant (F, F′) 24 hours post-fertilization (hpf) embryos were examined for expression of olig4 (red). (D-E′) In lateral views of the dorsal spinal cord, RNA in situ hybridization reveals expression of the interneuron marker olig4 (red). Green fluorescent protein (GFP)+ neurons do not express olig4 and comprise RBs and dorsal lateral ascending interneurons (see Figure 2). (F-F′) Islet1 knock-down leads to an increase in the number of olig4 expressing cells within the dorsal spinal cord. However, similar to RBs of control embryos (D-E′), RB-like neurons do not express detectable levels of olig4(F). (G-I) At 72 hpf, dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) are easily identified as GFP+ neurons with large somata located near the spinal cord/notochord border. (G, H) In control embryos, DRG neurons project from their soma bipolar axons that extend dorsally and ventrally (asterisks). (I) Islet1 knock-down reduces the number of GFP+ DRGs. Furthermore, for the few GFP+ DRGs remaining, their axons show abnormal morphologies. Scale bars = 50 µm in A (for A-C), D (for D-F′) and G (for G-I). CtlMO, 5-base mismatched; islet1(Sp)E3MO; E3MO, E3 morpholino; Uninj, uninjected.