Fig. 4
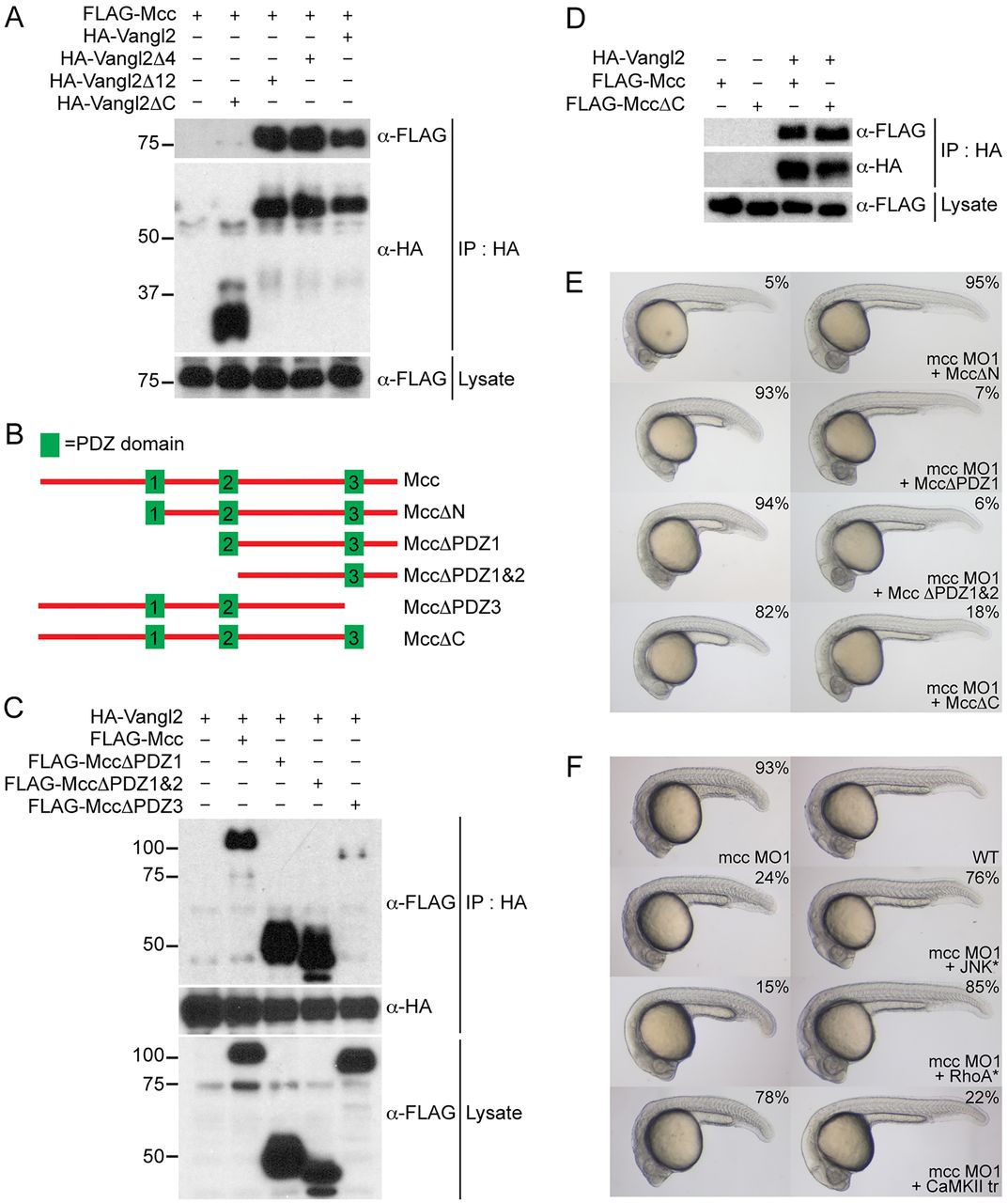
Mcc binds Vangl2 and acts upstream of RhoA and JNK. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation of FLAG-Mcc and HA-Vangl2 in HEK293 cells. Vangl2Δ4 (ΔETSV), Vangl2Δ12 and Vangl2ΔC correspond to increasing deletions of the Vangl2 cytoplasmic tail. Only Vangl2ΔC fails to precipitate FLAG-Mcc. Marker sizes (kDa) are indicated alongside. (B) Structure of wild-type mouse Mcc (top, not to scale) with three PDZ domains (green boxes) and assorted Mcc deletion constructs used for (C,D) immunoprecipitation and (E) zebrafish co-injection experiments. (C) HA-Vangl2 efficiently precipitates all Mcc deletion constructs except PDZΔ3, which lacks PDZ3 and the Mcc C-terminus. (D) HA-Vangl2 also efficiently binds MccΔC, which retains all three PDZ domains but lacks the extreme C-terminal ETSL type I PDZ interaction motif. (E) MccΔN mRNA rescues mcc morphants, whereas MccΔPDZ1, MccΔPDZ1&2 and MccΔC fail to complement loss of mcc, resulting in characteristic CE phenotypes. (F) Activated JNK* (MKK7B2Jnk1a1) and RhoA* (RhoA-G14V) but not CaMKII-tr rescue mcc morphants. The first row shows a representative mcc MO1 morphant (left) and an uninjected wild-type embryo (right) for reference. All embryos are at 1dpf. (E,F) MO and mRNA concentrations are provided in supplementary material Table S3. Phenotypic distributions are indicated as percentages, with scored embryo counts listed in supplementary material Table S4.