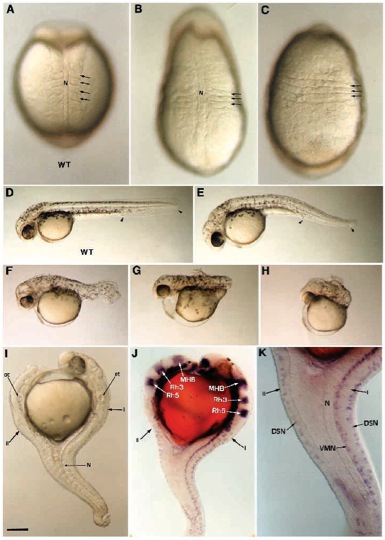
Fig. 3 Morphological defects generated by ectopic expression of FGF-8. A range of dorsalization phenotypes is obtained after FGF-8 RNA injection. At the beginning of somitogenesis, the embryos display an elongated shape and somites (arrows) expand laterally (B) or even fuse ventrally (C) compared to wild-type control in A. At 36 hours, weak phenotype is apparent as a small reduction in the tail region delimited with arrowheads (E), compared to wild type in (D). Phenotype of intermediate strength are represented by a shortened and twisted tail (F). Strong phenotypes are characterized by a deletion of the tail (G) or by a deletion of both trunk and tail (H). (I-K) A 36 hours old dorsalized embryo presenting a double axis (I, primary axis; II, secondary axis). (I) Anteriorly the secondary axis forms opposite to the primary axis while both are fused in the caudal portion. (J) Using Krox20 (Oxtoby and Jowett, 1993) and Eng3 (Ekker et al., 1992) reveal that the secondary axis develops up to the posterior midbrain. Anterior to this position, forebrain, anterior midbrain, olfactory placodes and optic vesicules are missing in the secondary axis. (J,K) The secondary axis is defective in notochord and floor plate. Ventral motor neurons (VMN) are missing while dorsal sensory neurons (DSN) labeled with Isl- 1 (Inoue et al., 1994) are present. MHB, midbrain-hindbrain boundary labeled with Eng3; N, notochord; ot, otic vesicles, rh3, rh5, rhombomeres 3 and 5 labeled with Krox20. (A,B) Dorsal views; (C) ventral view; (D-K) lateral views. Scale bar, 100 μm in A-C,K; 250 μm in D-J.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development