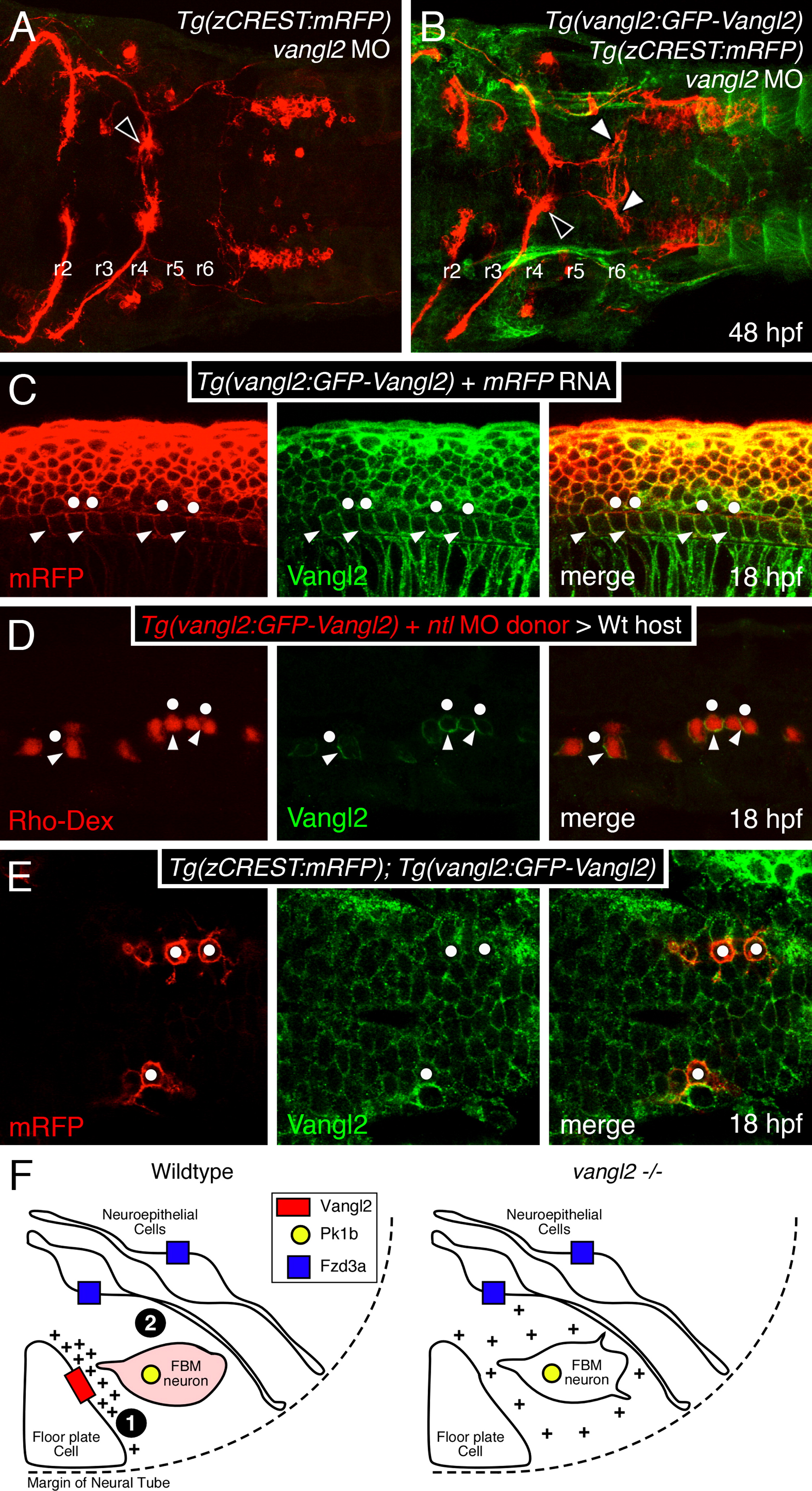
Fig. 8 Vangl2 is enriched in basolateral membranes of floor plate cells. Anterior is to the left in panels A–E. (A,B) Dorsal views of hindbrains processed for RFP and GFP immunostaining. In a control vangl2 morphant embryo (A), FBM neurons fail to migrate out of r4 (black arrowhead). In a Tg(vangl2:GFP-Vangl2) vangl2 morphant (B), many FBM neurons migrate out of r4 (white arrowheads). (C) Lateral view of an embryo processed for immunostaining to detect mRFP and GFP-Vangl2. Whereas mRFP is present on basolateral (arrowheads) and apical (dots) surfaces of floor plate cells, the apical surfaces are mostly devoid of GFP-Vangl2. (D) Lateral view of a host embryo containing donor-derived cells targeted to the floor plate, and processed for Rhodamine and GFP immunostaining. Donor-derived floor plate cells (Rho-Dex) exhibit basolateral enrichment of GFP-Vangl2 (arrowheads) with weaker signal at the apical surface (dots). (E) Dorsal view of the hindbrain showing uniform distribution of GFP-Vangl2 on the surface (mRFP) of FBM neurons (dots). (F) Model for regulation of FBM neuron migration by floor plate-derived Vangl2. In the wildtype rhombomere 4 hemi cross-section, Vangl2 on basolateral membranes of floor plate cells sequester a floor plate-derived orientating cue (+). Orientated protrusions on FBM neurons and associated signaling make them competent (primed; denoted by pink shading) to respond to other environmental cues (Step 1). These primed FBM neurons may respond to cell adhesive and/or cell repulsive cues in a Pk1b- and Fzd3a-dependent manner (Step 2), get excluded from the neuroepithelium in r4, and migrate caudally, as proposed previously (Wada et al., 2006). In rhombomere 4 of vangl2 mutants, the floor plate-derived cue does not get sequestered at the basolateral membranes of floor plate cells, and the FBM neurons do not become competent (Step 1 fails). The neurons are unable to respond to adhesive/repulsive cues on neuroepithelial cells, resulting in their integration into the neuroepithelium in r4 and consequent failure to migrate caudally. The depiction of Vangl2 and Fzd3a on floor plate and neuroepithelial cells, respectively, indicates their functional requirement for neuronal migration, and not their expression pattern, which is ubiquitous in the neural tube.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 382(2), Sittaramane, V., Pan, X., Glasco, D.M., Huang, P., Gurung, S., Bock, A., Li, S., Wang, H., Kawakami, K., Matise, M.P., and Chandrasekhar, A., The PCP protein Vangl2 regulates migration of hindbrain motor neurons by acting in floor plate cells, and independently of cilia function, 400-412, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.