Fig. S3
Expression Patterns of the gal4 Driver and UAS Effector Lines, Related to Figures 2 and 3
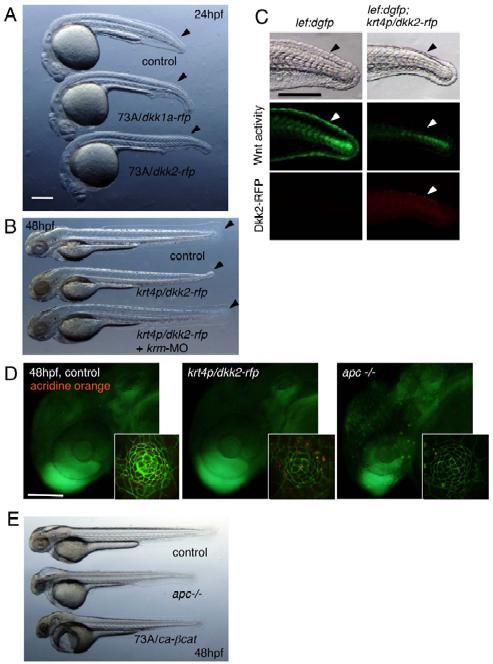
(A) The enhancer trap SAGFF73A (73A) line strongly expresses gal4 in the whole body. Overexpression of UAS:dkk1a-rfp or UAS:dkk2-rfp by the 73A line resulted in slightly enlarged heads as previously reported in overexpression of dkk1b [S1, S2]. Embryos also failed to form fin fold structures (arrowheads) as reported in embryos in which Wnt downstream signaling was deficient (tcf7 mutant embryos injected with lef1-MO) [S3]. Scale bar represents 100 μm.
(B) Overexpression of UAS:dkk2-rfp or UAS:dkk1a-rfp (not shown) in the skin affected fin fold formation, while the other parts of the body remains intact. Injection of krm-MO into the dkk2-overexpressing or dkk1a-overexpressing embryos (not shown) restored fin fold formation, consistent with the role of dkk and krm for inhibiting Wnt signaling.
(C) The krt4p:gal4 line expresses gal4 in the skin as shown previously [S4]. Overexpression of UAS:dkk2-rfp or UAS:dkk1a-rfp (not shown) abolished lef:dgfp expression in fin fold (arrowheads), confirming the role of these genes for inhibiting Wnt signaling. Scale bar represents 100 μm.
(D) Acridine orange staining does not detect apoptotic cells in neuromasts in dkk2-overexpressing embryos and apc mutant embryos. Scale bar represents 100 μm.
(E) Overexpression of UAS:ca-βcat-rfp by the 73A driver line causes severe defects in the brain similar to those of apc mutant embryos, suggesting that ca-βcat-rfp mimics constitutive Wnt signaling.